7.4.1
- Maritime Renewable Energy Alliance Center-Energy Turnover PBL Workshop 113年度海域再生能源聯盟中心-能源翻轉PBL工作坊 海域再生能源開發與海岸帶居民生活衝擊與調適
In the night state, images are not clearly recognized by computer vision. Therefore, this technology uses a UAV based a lidar to detect nighttime environmental information and recognize human characteristics. Using the background difference method and the algorithm of density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), the root mean square error and the surface state of the object are summarized as a condition to judge whether the object is human. The artificial intelligence algorithm of faster region-based convolutional neural network (Faster R-CNN) is used for skeleton recognition, and an automatic recognition system is established. As a result, the human-body recognition results of surface analysis and skeleton recognition are both up to 87.5 % in the nighttime environment. The website information of recognition results is established through the server terminal computer to present the current measured environmental state and recognize whether there is a human body in the nighttime environment. Eventually, the technology is applied to search the victims in the disaster relief environment and reduce the difficulty and time of night search and rescue.
Sustainable Impact: This technology employs LiDAR-equipped drones for nighttime detection, capable of identifying human features under low-light conditions to enhance disaster rescue efficiency and environmental monitoring. It aligns with SDG 13.3.1 by advancing education and technological application for climate adaptation and emergency response. The system's use of 3D surface fitting and spatial clustering supports SDG 14.2.1, contributing to coastal and terrestrial ecosystem monitoring. Through AI-based object recognition and data-sharing web platforms, it fulfills SDG 17.2.5's focus on interdisciplinary research collaboration and technological partnerships. Moreover, its energy-efficient, light-independent sensing capability exemplifies SDG 7.4.1, promoting innovative clean technology solutions for sustainable environmental management.
由於在夜間狀態下,電腦視覺無法明確判別物體的存在,然而光達可透過雷射掃瞄而不受光線影響。因此,本技術利用無人機以光達作為感測器主軸,以探測夜間環境資訊及辨別人體特徵。利用背景差分法和基於密度的空間聚類演算法(DBSCAN),透過曲面擬合計算出均方根誤差,歸納出物體表面狀態,作為判斷物體是否為人的一個條件。然後將其點雲資料進行影像處理,並以目標檢測法(Faster R-CNN)對形貌進行訓練及辨識,根據人體和物體特徵建立自動化辨識系統。最終,在夜間環境狀態下可即時測量出人體,並獲得最佳表面分析與骨架辨識成功率均有87.5%。並且透過伺服端電腦建立網站連結,呈現當下量測的環境狀態及識別環境是否存在人體,其效益可應用在救災環境下搜索罹難者,減少夜間搜救的困難及時間。
永續影響力: 此技術以光達搭載無人機進行夜間偵測,能在低光環境下辨識人體特徵,提升救災效率與環境監測能力,符合SDG 13.3.1推動氣候災害應變教育與技術應用的目標;同時,其環境掃描與地表曲面擬合分析有助於沿岸與陸地生態監測,呼應SDG 14.2.1對海洋與濱海系統的保護研究;此外,系統整合AI影像辨識與資料共享平台,展現SDG 17.2.5強調的跨領域技術合作;而其高效率、低照度運作特性亦符合SDG 7.4.1提倡的智慧能源與永續科技創新應用。
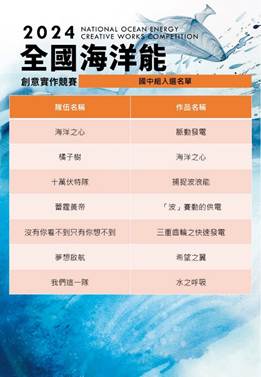

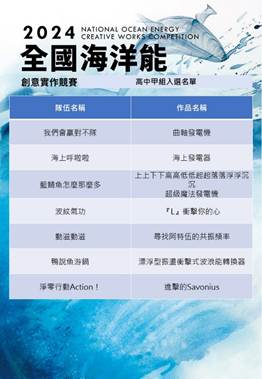

Evidence: https://www.facebook.com/energyntou/
- National Ocean Energy Creative Implementation Competition 全國海洋能創意實作競賽
f the Competition: Starting in the year 2016 (Republic of China 105), National Taiwan Ocean University, in collaboration with the Keelung City Government, jointly organized this competition and expanded it to include participants from national
Sustainable Impact: Since 2011, National Taiwan Ocean University has organized the Marine Energy Competition, focusing on wave and current energy converter design, efficiency optimization, and cost analysis. This long-standing event fosters innovation and hands-on learning among students, encouraging the application of marine energy technologies to support clean energy transitions. The competition strengthens awareness of renewable ocean energy's role in mitigating climate change while building practical engineering and sustainability skills. Moreover, it enhances collaboration between academia and industry in developing marine energy innovations. This initiative supports SDG 7.4.1 (clean energy promotion), SDG 13.3.1 (climate action education), SDG 14.2.1 (sustainable use of marine resources), and SDG 17.2.5 (partnerships for sustainable technology development).
海洋能源競賽的開始:自民國100年起,海洋大學開始舉辦海洋能源相關競賽。這競賽涵蓋了波能和流能轉換器的設計、效率計算、成本和安裝等領域。這個競賽已經持續多年,並取得了豐碩的成果。
永續影響力: 自民國100年起,國立臺灣海洋大學持續舉辦「海洋能源競賽」,主題涵蓋波能與流能轉換器設計、效率分析、成本評估與安裝技術等領域。活動旨在培育學生的創新思維與實作能力,促進海洋再生能源技術的發展。透過競賽形式,學生得以實踐工程理論,並理解海洋能源於減緩氣候變遷及永續能源轉型中的關鍵角色。活動亦促進學術與產業界在永續技術研發上的交流合作。此舉落實 SDG 7.4.1「推廣潔淨能源技術」、SDG 13.3.1「提升氣候行動教育」、SDG 14.2.1「保育與永續利用海洋資源」及 SDG 17.2.5「強化夥伴關係推動永續科技創新」。

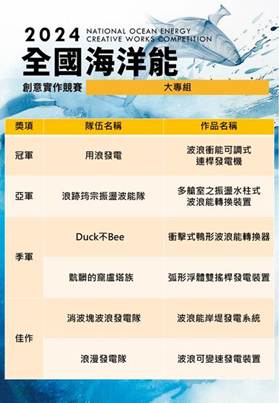

Evidence: https://www.facebook.com/energyntou/
