14.2.2
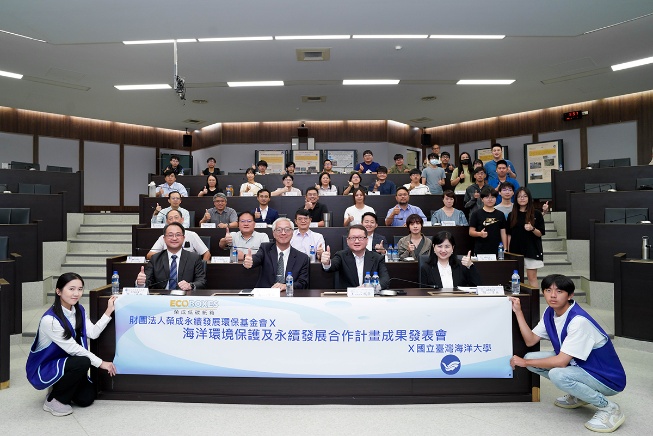
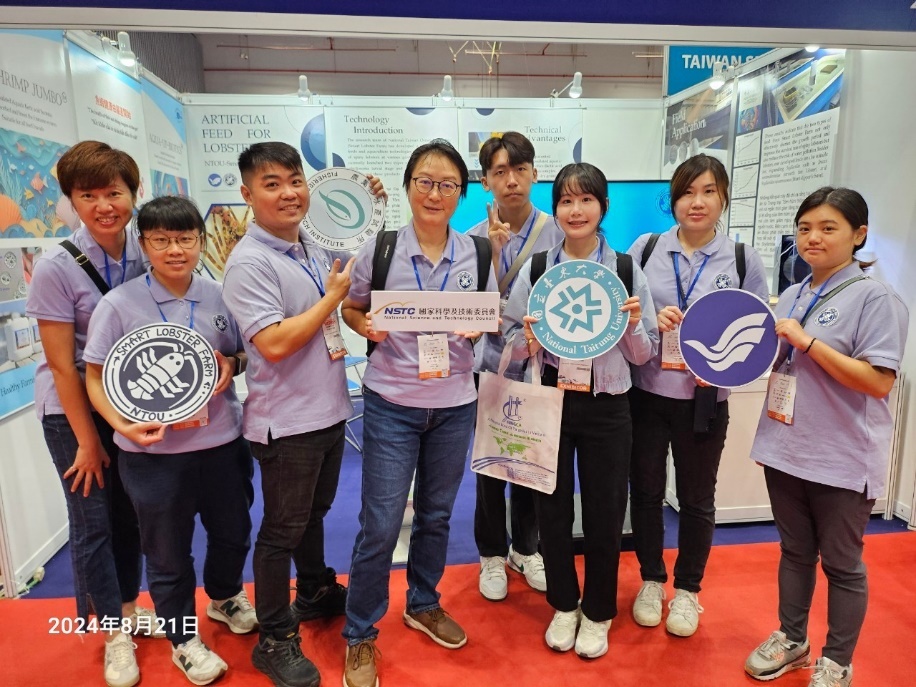
1. 2024 Longchen Paper & Packaging Co., Ltd. and National Taiwan Ocean University Joint Project Results Presentation Conference
2024財團法人榮成永續發展環保基金會與國立臺灣海洋大學合作計畫成果發表會
Since 2019, National Taiwan Ocean University and Longchen Paper & Packaging Co., Ltd. have jointly launched a collaboration project on Marine Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development. Each year, Longchen Paper & Packaging Co., Ltd. has provided over NT$2 million in funding to support the implementation of related programs at our university. In 2024, marking the fifth anniversary of this partnership, a Results Presentation Conference was held at our university to showcase and promote the achievements of the collaboration. The event was attended by approximately 80 participants, who listened to the project outcomes. To date, 29 students have taken part in the program, deeply embedding the concept of sustainable development in their minds and actions.
Sustainable Impact:Since 2019, the university has partnered with the Rongcheng Foundation for Sustainable Development to implement projects on "Marine Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development," with over NT$2 million in annual funding. Over five years, this collaboration exemplifies SDG 17.2.5 through a long-term public–private partnership advancing marine sustainability. The initiative integrates marine ecosystem protection (SDGs 14.2.2, 14.2.3), ocean research and education (14.3.1, 14.3.3), sustainable fisheries management (14.4.2, 14.4.3), and conservation area promotion (14.5.2), while also fostering climate awareness (13.3.5). The 2024 results symposium showcased achievements to around 80 attendees and engaged 29 students in hands-on projects, embedding sustainability values and demonstrating the power of academia–foundation collaboration in advancing marine conservation and climate education.
本校與財團法人榮成永續發展環保基金會自2019起開展「海洋環境保護及永續發展」合作案,由榮成永續發展環保基金會每年提供超過200萬元經費供本校執行相關計畫。2024年雙方合作滿5年,故決定於本校舉辦成果發表會,推廣合作成果。 發表會當日共有約80人出席聆聽計畫成果,本合作更已有29位學生參與計畫,將永續發展的觀念深植於心。
永續影響力:本校自2019年與榮成永續發展環保基金會合作推動「海洋環境保護及永續發展」計畫,每年投入逾200萬元資源,持續五年推展海洋教育與保育行動,展現公私協力落實SDG 17.2.5「建立長期夥伴關係」。計畫內容涵蓋海洋生態保育(14.2.2、14.2.3)、海洋研究與教育推廣(14.3.1、14.3.3)、漁業與資源永續利用(14.4.2、14.4.3)、以及海域保護區推動(14.5.2),並融入氣候行動教育(13.3.5)。成果發表會除促進知識分享,也吸引29位學生參與,深化永續素養與行動實踐,展現學界與基金會共同推動海洋永續的成效。


Evidence:
https://research.ntou.edu.tw/p/412-1021-12463.php?Lang=zh-tw
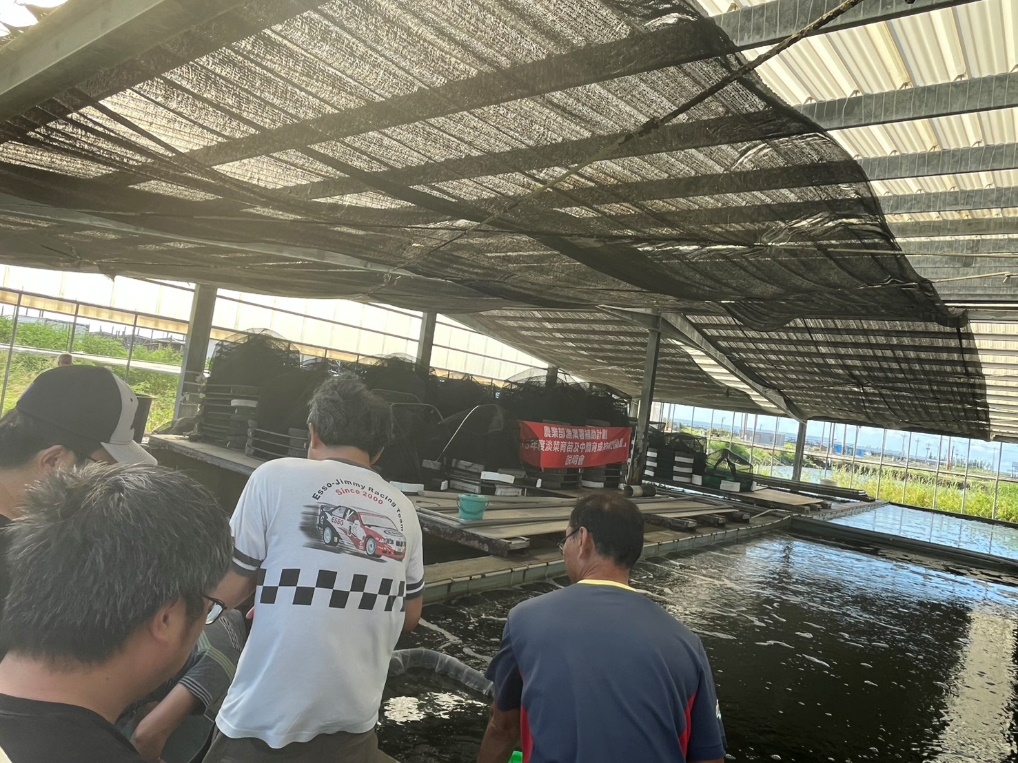
2. Development of Mussel Seedling and Intermediate Breeding Technology
淡菜育苗及中間育成技術開發
In cooperation with the Fisheries Agency of the Ministry of Agriculture and the Lienchiang County Government, the Bachelor's Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology has been engaged in aquaculture-related research in the Matsu region since 2021. The initiative aims to strengthen the transformation of the local seafood sales model and enhance the food safety of aquatic products in the area. With its excellent water quality, Matsu produces mussels of superior quality compared to those from Taiwan's main island, giving it a competitive edge over imported products. As a result, Matsu has become Taiwan's largest mussel farming region. The Zhoushan Archipelago in China has a well-established mussel seed industry with mature breeding techniques. Due to Matsu's geographical proximity to the aquaculture areas of Fujian Province, local farmers have long relied on purchasing mussel seeds from across the strait. However, the Chinese authorities lack proper source control over the mussel industry, posing potential food safety risks to Taiwan's mussel supply chain. Therefore, it is necessary to leverage Taiwan's advanced bivalve breeding technologies to establish a long-term mussel hatchery base in Matsu, ensuring both industrial autonomy and food safety stability. This project is a continuation of previous research efforts. In 2023, the team successfully established preliminary techniques for mussel seed cultivation, completed local seed collection and intermediate culture trials, and set up onshore aquaculture facilities in Beigan, Matsu. The feasibility of mussel hatchery operations has been verified, and collaboration experience with local growers has been accumulated. Building on the 2023 outcomes, the 2024 project will further examine the reproducibility and mass production potential of mussel seed cultivation, while collecting comprehensive data on reproduction and growth to establish a stable intermediate culture system. On the technical front, the project will continue refining artificial mussel larval incubation methods and organize a “Technical Development Seminar and On-Site Demonstration on Mussel Seed Cultivation and Intermediate Culture,” inviting Matsu aquaculture farmers and representatives from the Fisheries Agency to participate. By leveraging Taiwan's aquaculture expertise, the project seeks to help Matsu produce mussel seeds locally, forming a production and marketing model of “Taiwan hatchery – Matsu grow-out – Taiwan sales.” This approach will reduce capital expenditure and transportation costs while utilizing existing marketing and logistics infrastructure to minimize the need for new channel development. In the mid- to long term, the project will expand local aquaculture capacity in Matsu to prepare for the establishment of a permanent hatchery base capable of supplying sufficient mussel seeds to local producers, thereby promoting sustainable industry development. With the establishment of mussel seed cultivation facilities, the project is expected to directly create job opportunities in aquaculture and nurture skilled professionals for the field. The localized breeding research outcomes can also be applied to develop modular aquaculture systems, support fishermen's career transitions, and facilitate fishery transformation, driving the overall upgrading and promotion of Matsu's aquaculture industry. From a social impact perspective, localized mussel seed cultivation is a crucial step in implementing the Lienchiang County Seafood Certification and Labeling System. Through a fully traceable production process—from seed, grow-out, to sales—the project aims to realize a transparent and verifiable “from seed to table” model. This integrated traceability system will strengthen risk management efficiency, enhance food safety assurance, and improve the brand image of Matsu mussels, establishing a new benchmark for sustainable and safe aquaculture in the region.
Sustainable Impact: The university’s Department of Marine Biotechnology collaborates with the Fisheries Agency and the Lienchiang County Government to establish a sustainable mussel hatchery program in Matsu. This initiative exemplifies SDG 14.2.2 and SDG 17.2.1, promoting sustainable aquaculture and partnership with local government.
By developing independent mussel seed production and mid-stage cultivation technologies, the project enhances Taiwan’s aquaculture self-sufficiency while ensuring food safety and ecological balance. The collaboration integrates governmental, academic, and industrial expertise to improve water resource management, strengthen local fisheries’ competitiveness, and create job opportunities in the marine biotechnology sector.
Through transparent traceability systems—from hatchery to market—the project supports a sustainable “seed-to-table” supply chain, advancing both environmental stewardship and economic resilience. It demonstrates how cross-sector collaboration between higher education and government can drive regional innovation and sustainable blue economy development in line with the goals of SDG 14 and SDG 17.
海洋生物科技學士學位學程配合農業部漁業署及連江縣政府合作,為強化臺灣馬祖地區水產品銷售模式轉型,並提升馬祖水產品之食用安全性,自2021年起即投入馬祖地區水生生物養殖相關研究。馬祖地區水質優良,所出產之淡菜成貝品質相對臺灣本島更佳,具備與進口產品競爭的優勢,因此目前馬祖已成為臺灣最大的淡菜成貝養殖地。 由於中國舟山群島一帶淡菜種苗產業聚落龐大,其種苗培育技術亦相當成熟,馬祖鄰近大陸福建養殖區,長期以來多向當地購買淡菜種苗。然而中國當局對淡菜產業並無完善的源頭管控,造成進口種苗在食用安全上存在風險,對我國淡菜產業影響甚鉅。為此,有必要運用臺灣在二枚貝種苗培育上的技術優勢,於馬祖設立長期運作的淡菜育苗基地,以供應當地業者使用,確保產業自主與食安穩定。 本計畫為延續性計畫。2023年度已初步建立淡菜種苗育苗技術,並完成馬祖在地淡菜苗體之採集與中間育成技術驗證,目前已於馬祖北竿地區建置陸上養殖設施,並確認淡菜育苗之可行性,具備與當地業者合作進行貝類中間育成的經驗。2024年度計畫將以2023年成果為基礎,持續探討淡菜育苗再現性與量產技術,並蒐集完整的繁殖及生長數據,以建立穩定的中間育成技術。 在技術層面上,計畫將持續改良人工孵育淡菜苗體之技術,並舉辦「淡菜育苗及中間育成技術開發說明會暨現勘活動」,邀請馬祖地區養殖業者及漁業署共同參與。預期藉由臺灣本島之水產技術優勢,協助馬祖產出淡菜種苗,形成「臺灣育苗、馬祖養成、臺灣銷售」的產銷鏈模式。此一模式可降低資本支出與運輸成本,並可依循既有的行銷與物流系統,減少新通路建置的負擔。中長期而言,將逐步擴增馬祖地區原有的養殖設備,為設置長期育苗基地做準備,達成穩定供應在地業者種苗的目標,促進整體產業的永續發展。 未來將隨著淡菜種苗培育場域的建立,預計可直接創造水產養殖業的就業機會,並培育專業人才投入相關領域,生產足夠之種苗以供應馬祖在地業者。同時,育苗技術自主化的研究成果亦可應用於養殖模組開發,進一步輔導漁民轉業及推動漁業轉型,帶動馬祖養殖產業升級與推廣。 此外於社會影響層面,淡菜在地自主培苗是連江縣落實水產品證明標章制度的重要關鍵。透過從種苗、掛養到銷售的一貫履歷作業,將可實現「從種苗到餐桌」的公開透明與可追溯機制,建立完善的風險管理體系,強化連江縣淡菜食品安全與品牌形象,為馬祖地區打造兼具產業效益與食安保障的水產新典範。
永續影響力:本校海洋生物科技學程與農業部漁業署及連江縣政府合作推動馬祖淡菜育苗基地計畫,屬於 SDG14.2.2 與 SDG17.2.1 之具體實踐。此計畫結合政府與學研能量,推動在地水產養殖技術自主化,促進區域產業轉型與永續經營。透過改良淡菜種苗培育技術與建立育成體系,不僅強化水域生態管理與食安追溯機制,也深化地方政府夥伴關係。計畫成果有助於提升產業韌性、促進在地就業,實現永續漁業與地方共榮的目標。


Evidence:
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/279782014.pdf
3. Environmental Education Series: Sustainable Oceans & Circular Resources
「永續海洋-循環資源」系列環境教育活動
Sustainable use of marine resources has become a global consensus. Through marine environmental education, we convey concepts and hands-on practices in biological resource restoration, the circular economy, water safety, and the hazards of microplastics. Centered on the ethos of "clean the sea, understand the sea, get close to the sea, and enter the sea," our marine science outreach—combined with activities such as stock-enhancement releases and seed-stock cultivation—advances marine environmental policies and the goals of resource circularity. We completed 43 marine education sessions with a total of 3,156 participant attendances. Program content spanned coral introduction and conservation, coral planting and restoration, algae literacy, stock releases to coastal waters, microplastic hazards, fish and seaweed food education, coastal cleanups, geological field surveys, and on-water experiential activities.
Sustainable Impact:This initiative, centered on "Clean the Sea, Know the Sea, Approach the Sea, Enter the Sea," integrates ecological restoration, coral conservation, and microplastic awareness through experiential learning. It fulfills SDG 13.3.1 by promoting climate and environmental education, and SDG 13.3.5 through partnerships with NGOs on climate-related outreach. Activities such as coral propagation, marine species release, and pollution awareness align with SDG 14.2.2, 14.2.3, 14.3.1, and 14.3.3, which emphasize ecosystem restoration and pollution reduction. Additionally, coastal cleanups and coral planting support SDG 14.5.2 on marine conservation. The 43 public courses and hands-on experiences also correspond to SDG 4.3.4, representing off-campus educational outreach that enhances ocean literacy and encourages sustainable community engagement.
海洋資源永續利用已成為國際共識,透過海洋環境教育傳遞生物資源復育、循環經濟、水域安全及微塑膠危害之觀念與實際體驗,以「淨海、知海、近海、進海」為核心進行海洋科普教育,並搭配生物放流與種苗培植等活動,可落實海洋環保政策之推動與資源循環利用之目標,完成43場次之海洋教育課程,共計3156人次,活動內容涵蓋珊瑚介紹及保育、珊瑚種植復育、藻類知識科普、海域放流、微塑膠危害、食藻教育、海岸淨灘、地質踏查、食魚文化、水上體驗等一系列活動。
永續影響力:此活動以「淨海、知海、近海、進海」為主軸,結合生物復育、珊瑚保育與微塑膠防治等教育體驗,屬於SDG 13.3.1的氣候教育推廣及13.3.5與NGO合作推動氣候行動之實踐。同時透過海洋資源復育與生物放流,符合SDG 14.2.2、14.2.3及14.3.1、14.3.3對保護與復育海洋生態系及減少海洋污染的目標;再者,海岸淨灘與珊瑚種植亦落實SDG 14.5.2之海洋保護行動。而多場公眾課程與體驗教育則對應SDG 4.3.4之校外教育外展,推動全民海洋素養與永續行動。


Evidence:
https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=1781814792357038
https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=465669422909823
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cZoxPo4zIw8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0LIpe_Lx1Zo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=POkOR121aWc
4. Cultivation Center for Aquatic Organisms Promotes Seaweed Breeding and Conservation
「海洋生物培育館」推動海藻育種與保育
In response to the university's growing needs for algae development and utilization, marine organism cultivation, breeding, and live experimental research, the Center of Excellence for the Oceans (CEO) collaborated with the Rising Sun Education Foundation in 2019 to establish a large-scale Cultivation Center for Aquatic Organisms on campus. The construction was funded by a NT$20 million donation from the Foundation, while the CEO is responsible for its management and operation. The Cultivation Center for Aquatic Organisms, with a total floor area of approximately 500 ping (about 1,650 m²), houses the Taiwan International Algae Research Fund (TIARF), which primarily promotes research on the cultivation and utilization of macroalgae. The Center enhances the university's capacity in marine biology and aquatic technology research, and is also open for visits by governmental institutions and educational organizations, serving as a public platform for marine science education and outreach. By the end of 2024, the Center had successfully cultivated and preserved 45 species of macroalgae, including: • Green algae (21 species) such as Caulerpa lentillifera, Caulerpa racemosa var. laetevirens, Ulva lactuca, Ulva reticulata, and Codium fragile; • Brown algae (7 species) such as Sargassum horneri, Sargassum siliquastrum, Ecklonia cava, and Padina arborescens; • Red algae (17 species) including Gracilaria spp., Kappaphycus alvarezii, Eucheuma denticulatum, Porphyra spp., Gelidium spp., and Ahnfeltia plicata. In addition, several economically valuable species, such as Gracilaria coronopifolia and Codium fragile, have been used for seedling technique development, while Ulva prolifera, Porphyra, and Laminaria are preserved in different reproductive forms, such as filamentous and protoplast stages. In 2024, the total macroalgae production reached 545.6 kg, of which 268 kg were provided through academic collaborations. Besides internal use by the university, 31 batches of samples were supplied to National Cheng Kung University, Academia Sinica, and private industry partners for studies on natural product analysis, algal product development, and marine aquaculture applications. In the same year, the Center received 46 visiting groups totaling 799 visitors, including representatives from the National Academy of Marine Research, the National Science and Technology Council, as well as professors from Japan, France, the United States, and the Philippines, who visited to experience the algae cultivation facilities of the Cultivation Center for Aquatic Organisms.
Sustainable Impact:The collaboration between the Marine Center and the Sunrise Education Foundation to establish the "Marine Life Cultivation Hall"demonstrates strong alignment with SDG 14.2.2 by restoring and sustainably utilizing coastal and marine ecosystems through large-scale seaweed preservation and cultivation. The facility's educational outreach and research dissemination correspond to SDG 14.3.1, emphasizing marine science education and awareness. Furthermore, by sharing cultivated species and technologies with universities, research institutes, and industries, it fulfills SDG 14.3.3, which promotes research cooperation and knowledge exchange on marine resources. This initiative embodies the integration of academia, industry, and the public in advancing sustainable marine development and biodiversity conservation.
因應學校發展藻類開發利用、海洋生物培育、育種與活體試驗需求增加,海洋中心與財團法人旭日教育基金會合作於2019年在校內增建大型海洋生物飼育設施「海洋生物培育館」,由基金會捐款2,000萬元建造工程費用,海洋中心負責管理營運。「海洋生物培育館」總樓地板面積約500坪,館內設置「臺灣國際藻類研究基金委員會」,主要推動大型藻類的培育與開發利用研究。「海洋生物培育館」強化海洋生物及水產科技的研究,同時開放機關團體預約參觀,提供社會大眾認識水生生物的場館,推廣海洋教育。 至2024年底,養殖藻種計有綠藻21種(小葉蕨藻、長莖葡萄蕨藻、針葉蕨藻、總狀蕨藻大葉變種、大野石蓴、網石蓴、滸苔、法囊藻、偏腫法囊藻、氣生硬毛藻、青海菜、羽藻、仙掌藻、帚狀法囊藻、香蕉菜、杉葉蕨藻、趨化蕨藻、舌葉蕨藻、可食松藻、大葉仙掌藻、萊氏仙掌藻)、褐藻7種(冬青葉馬尾藻、銅藻、羊栖菜、大團扇藻、圈扇藻、扇形棕葉藻、錫蘭網地藻)及紅藻17種(海木耳、卡帕藻、麒麟菜、黃氏葉膜藻、紅翎藻、紅葡萄藻、臺灣海膜(平展海膜)、殼狀珊瑚藻、皮絲藻、弓龍鬚菜、糾結龍鬚菜、張氏龍鬚菜、可食龍鬚菜、縊龍鬚菜、麒麟龍鬚菜、海人草、金膜藻)等三大類,合計45種大型海藻的保種及擴大培養;此外,數種具有經濟價值之大型海藻,如雞冠菜、纖細松藻等藻種,進行培苗技術建立;另有青海菜、紫菜、海帶等大型海藻,以絲狀體、原生質體等不同形式的繁殖體藻體保存。2024年大型海藻總產量達545.6Kg,其中268Kg以學術合作名義,除提供本校使用外,亦提供國立成功大學、中央研究院、民間業者等單位索取計有31批次,分別進行天然物分析、藻類產品開發與海上養殖使用。2024年共計有校內、外貴賓、各級學校、業界等單位參訪,共計46場次799人參觀。包含國家海洋研究院,國科會,以及日本、法國、美國、菲律賓等大學教授來訪,體驗海洋生物培育館之藻類場域。
永續影響力:本案由海洋中心與基金會合作設立「海洋生物培育館」,進行大型海藻保種、繁殖與技術開發,具體落實SDG 14.2.2中「推動海洋與沿岸生態系復育及永續利用」的目標。館內研究與展示活動推廣藻類應用與保育知識,對應SDG 14.3.1強調「提升海洋科學研究與教育宣導」。此外,藉跨校與產業共享藻種資源及技術,促進藻類產品開發與海上養殖應用,符合SDG 14.3.3「推動海洋資源研究合作與知識分享」,展現學術、產業與社會共創的永續發展實踐。


Evidence:
https://mprp.ntou.edu.tw/p/404-1017-97847.php?Lang=zh-tw
5. The 54th issue of Fisheries Extension Report Published
出版海大漁推54期
The Fisheries Extension Committee publicly solicits manuscripts from experts and scholars in related fields, and publishes the "Fisheries Extension Report" science journal on a regular basis every year and sends them to various high schools libraries, district fishermen s associations or the general public for free, in order to raise awareness of overfishing, illegal, unreported and awareness of unregulated fishing and destructive fishing practices, for sustainable fisheries production.
Sustainable Impact:The Fisheries Promotion Committee annually publishes the popular science journal NTOU Fisheries Extension, inviting experts and scholars to contribute articles. The publication is distributed free of charge to high school libraries, regional fisheries associations, and the general public to raise awareness of overfishing, IUU (illegal, unreported, and unregulated) fishing, and destructive fishing practices. This initiative aligns with SDG 14.2.2 by promoting education and awareness on sustainable fisheries and marine ecosystem management. It also fulfills SDG 4.3.1 by providing accessible learning resources to students and communities. Through science communication and outreach, the university transforms academic research into public education, fostering collective understanding and action toward sustainable marine resource use.
漁業推廣委員會公開向相關領域專家學者徵求稿件,於每年定期出版「海大漁推」科普期刊免費寄送至各高中職圖書館、區漁會或一般民眾,以提高對過度捕撈,非法、未報告和無管制捕撈以及破壞性捕撈做法的意識,達到漁業持續性生產的目的。
永續影響力:漁業推廣委員會每年定期出版《海大漁推》科普期刊,透過專家學者撰稿,向高中職學校、漁會及民眾免費寄送,提升社會大眾對過度捕撈、非法與破壞性漁業行為的認識。此舉不僅促進永續漁業管理意識,落實 SDG 14.2.2 「加強海洋生態與資源保育教育」,同時也實現 SDG 4.3.1「確保所有人享有包容與可近的教育機會」。藉由知識傳遞與社會教育推廣,使大學研究成果真正轉化為全民海洋環保行動力。


Evidence:
6. Quantity Estimation for Fish in an Indoor Pond Using Multiple Imaging Sonar Systems, Density Maps, and Bayesian Estimation
使用多部成像聲納系統、密度圖技術與貝氏估計估算室內養殖池中的魚隻數量
In a small coastal research facility, a group of engineers and marine scientists gathered around a tank filled with glimmering fish. It seemed ordinary at first glance, but this scene represented a long-standing challenge in aquaculture—how to count fish accurately, efficiently, and without harm. For decades, fish farmers have relied on manual counting, a tedious process requiring laborers to scoop fish or use cameras in ideal conditions. This approach is slow, error-prone, and stressful for the fish. When natural disasters such as typhoons cause mass mortality, aquaculture operators are required to submit accurate counts for government subsidies and third-party audits—yet existing methods often fail to provide reliable, verifiable data. This urgent need for precision, transparency, and efficiency became the spark for a new idea: an AI-powered, sonar-based fish counting system that could operate automatically, in real time, and under any water condition. From Challenge to Vision The research team set out with a clear goal: to develop a non-contact, real-time, and objective fish counting method suitable for indoor aquaculture ponds. Their vision was to replace traditional manual estimation with a fully automated system that combined multi-beam imaging sonar, deep learning-based density estimation, and statistical modeling. The first obstacle they faced was environmental. Unlike clear laboratory tanks, real aquaculture ponds often have turbid water and low light, making optical cameras ineffective. To overcome this, the team turned to sonar imaging, which uses sound waves instead of light and works perfectly in turbid environments. Multiple sonar devices were deployed around the pond from different angles to widen the sensing range and reduce blind spots. But having multiple sonar feeds created another problem—overlapping views. Fish detected by one sonar could easily appear again in another, leading to double-counting. To solve this, the researchers adopted density-map technology and applied the Monte Carlo method to analyze sonar coverage and and to understand how overlapping areas affected accuracy. Once the sonar images were obtained, they were converted into density maps, a representation where each pixel's intensity corresponded to the number of fish likely present in that area. These maps from different sonar perspectives were then fused together, reducing duplication and improving precision. The Intelligence Behind the System After obtaining multi-view sonar images, the team applied neural network techniques to transform and fuse them into a single density map. This not only expanded the effective sensing range of the sonar but also prevented double counting of fish. However, the ocean never behaves predictably. Fish respond to feeding, temperature changes, and disturbances, often clustering or scattering unpredictably. These behavioral anomalies could easily distort the data. Thus, the researchers identified and excluded abnormal behavioral patterns and focused on “normal” conditions. As a result, the model produced more stable and representative estimates. Results That Redefined Efficiency After months of field testing in indoor aquaculture ponds, the results were clear. The proposed system operated at 2.67 times the efficiency of manual counting, significantly reducing the time required to manage multiple ponds. Over a 10-year period, the system was projected to lower total operational costs by 23%, making it ideal for facilities requiring frequent estimations. Beyond economics, the benefits extended to animal welfare and data integrity. The sonar-based system eliminated the need to net or disturb fish, reducing physical stress and injury. It also provided real-time digital records, allowing farmers and auditors to access transparent, verifiable data anytime. Moreover, because the system's results are based on algorithmic calculations rather than human judgment, they are objective and consistent, minimizing potential bias during government inspections or third-party certification. For large-scale or long-term aquaculture operations, this represented not just a tool—but a transformative management solution. Conclusions and Future Outlook This study presents a comprehensive, non-contact, real-time, and data-driven fish counting framework for indoor aquaculture ponds. By integrating multi-beam sonar imaging, density mapping, weak annotation, behavioral filtering, and statistical estimation, the system overcomes the limitations of single-view sonar—such as occlusion and duplicate counting—and achieves high accuracy and temporal stability across different time periods and environmental conditions. Field experiments demonstrated the method's robustness and economic feasibility, making it a strong candidate for deployment in large aquaculture facilities. However, the researchers envision several directions for future development. In the next phase, the team plans to create an end-to-end integration of statistical estimation and neural networks, adding a specialized statistical inference layer capable of learning both local density and global population simultaneously. By incorporating higher-level features—such as spatial block distribution and view-weight adjustments—the system could further reduce uncertainty in estimations. Another future goal is to develop an automated calibration mechanism that can self-adjust sonar positioning without disturbing the fish, increasing both precision and ease of deployment. From an application perspective, the system could be expanded to net cages, semi-open ponds, or offshore aquaculture with environmental adaptations for different fish species and water conditions. Ultimately, this approach paves the way for an AI-assisted aquaculture monitoring ecosystem—one that enables sustainable management, reduces labor, and enhances transparency across the industry. A Glimpse Into the Future As the final tests concluded, the sonar units quietly pulsed beneath the water's surface, mapping every movement in sound. On the lab's central monitor, a digital counter flickered—numbers rising and stabilizing as the system confirmed the estimated population. For the team, it was more than a number. It represented the convergence of marine science, artificial intelligence, and sustainability. What began as a problem of counting fish had evolved into a step toward a smarter, more humane, and data-driven aquaculture future—one where technology listens to the ocean and helps humanity care for it more wisely.
Sustainable Impact:This research presents an innovative AI-based fish counting system that integrates imaging sonar, neural networks, and Monte Carlo optimization to achieve non-invasive, real-time, and highly accurate estimation of fish populations. Unlike traditional manual counting, which is time-consuming and stressful to fish, this system leverages multi-angle sonar imaging and density map modeling to prevent double-counting and enhance detection accuracy even in turbid or low-light conditions. Experimental results demonstrate a 2.67× efficiency improvement over manual methods and a 23% reduction in long-term operational costs. By ensuring objective, verifiable data collection, the system supports fair decision-making in policy subsidies, aquaculture insurance, and production auditing. Moreover, its non-contact design minimizes ecological disturbance, advancing animal welfare and ecosystem sustainability. This achievement exemplifies the integration of artificial intelligence, marine science, and sustainable aquaculture, directly contributing to SDG 14.2.2: Conservation and sustainable use of marine and coastal ecosystems.
在寧靜的養殖研究中心裡,一群工程師與海洋科學家正注視著一池游動的魚群。這看似平凡的畫面,其實隱藏著一個長久以來困擾養殖業的難題——如何準確、快速、且不傷害魚隻地進行魚群數量估算? 在傳統漁業管理中,人工數魚是最常見的方法。人員需撈網、拍照、或依序觀察影像逐一記錄魚數。這樣的方式不僅耗時、受天候與環境條件限制,還容易造成魚群驚嚇與受傷。而當天災導致大量魚隻死亡時,養殖戶需向政府申請補助,卻常因缺乏公正、客觀的數據依據而面臨困難。這樣的現實,促使研究團隊萌生了一個全新的構想——能否運用人工智慧與聲納技術,打造出一套非接觸、即時且客觀的魚隻估算系統? 問題的起點:從人工誤差到智慧化構想 研究的出發點十分明確:開發一套能在任何環境條件下準確估算魚數的系統。團隊首先鎖定了傳統光學攝影的侷限——在水質混濁、光線不足的情況下,攝影鏡頭往往無法辨識魚體輪廓。為此,研究團隊選擇以「成像聲納(Imaging Sonar)」作為主要感測技術,藉由聲波穿透水體的特性,即使在低光或高濁度環境下,也能清楚描繪魚群分布。 為了擴大觀測範圍並降低盲區,系統部署了多部聲納裝置,從不同角度捕捉影像。然而,多視角的優勢也帶來了挑戰——魚體在不同角度下可能被重複偵測,導致重複計數(Double Counting)。為解決這一問題,研究團隊引入了密度圖(Density Map)。並使用蒙地卡羅方法(Monte Carlo Method),分析各聲納的覆蓋範圍與感測比例,進一步優化配置,確保估算更準確。 技術突破:從聲納影像到AI智慧計數 獲得多視角聲納影像後,團隊使用神經網路技術將其轉換並融合為一張密度圖。如此,不僅可以擴增聲納感測範圍也避免魚重覆計算。同時,魚群的行為變化——例如受到餵食、聲音或光線驚擾——常導致影像中出現異常的分布型態。為了排除這些行為異常所造成的偏差,研究團隊對魚群動態進行分析,辨識出異常行為影像並排除在估算之外,確保結果的穩定性與可靠性。 研究成果:效率、準確與公正的平衡 經過多次實地測試與驗證,系統在不同日期與時段皆展現出穩定且高準確的表現。結果顯示,此智慧化系統的效率為人工方法的2.67倍,可顯著縮短多池操作的時間。從長期經濟效益分析來看,單次估算成本與十年總成本相比,系統能節省約23%的支出。 此外,由於系統採用非接觸式量測方式,魚群不再因撈取與干擾而受傷,減少了養殖過程中的壓力與死亡風險。同時,所有的數據皆以數位方式記錄,形成可追溯、可稽核的資料基礎,方便日後的管理與第三方驗證。 更重要的是,系統的估算結果完全建立在演算法與數據模型上,避免了人為主觀判斷的誤差,使其在政策補助審查、產量統計或保險理賠等情境中,能提供公正且具說服力的依據。 結論與未來展望:從智能養殖走向永續藍海 本研究成功提出一套結合多部成像聲納、密度圖神經網路、弱標註學習、行為分析與統計推估的智慧魚隻計數方法。實驗結果證實,此系統能在不同環境條件下保持高準確度與穩定性,特別適合應用於大型室內養殖池與長期監測場域。 展望未來,研究團隊將持續推進技術整合。此外,未來若能發展自動化校正機制,即使不干擾魚群,也能持續優化聲納融合準確度。 最終,當聲納的波紋在水中擴散、回收成一張又一張密度圖,螢幕上的數字不只是數量,而是科技理解生命的語言。 這項研究讓人們看見,未來的養殖不再只是生產,更是結合人工智慧、永續思維與海洋科學的一場革命——一場從「數魚」開始,卻遠遠超越「數魚」的藍色創新。
永續影響力:本研究以人工智慧結合成像聲納技術,開發出一套非接觸式、即時且高準確度的智慧魚群估算系統,成功解決傳統人工數魚耗時、誤差高、且易造成魚群受傷等問題。系統利用多部成像聲納進行多視角觀測,並藉由神經網路生成密度圖與蒙地卡羅方法修正重覆計數,達成高效率與高準確度的魚數估算。此技術的效率為人工方法的2.67倍,並能降低23%長期成本,兼具經濟效益與生態友善特性。非接觸式監測不僅減少魚隻壓力與死亡率,也透過數位化資料建立公正、可追溯的漁業管理依據。此成果不僅提升養殖科技智慧化與永續性,更有助政府補助、保險理賠及資源管理制度化,符合SDG 14.2.2「保育與永續利用海洋生態系」之核心精神。
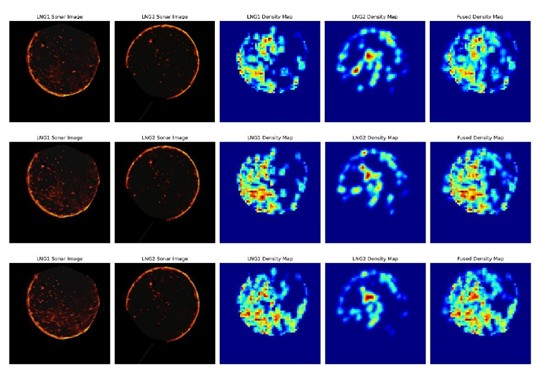
Evidence:
https://hdl.handle.net/11296/m9358t
7. Coral Primary School
珊瑚小學堂
New Taipei City Marine Coral Education Promotion Project for 2024, subsidized by the Ocean Affairs Council, the New Taipei City Government will offer eight free Coral Primary school sessions every Saturday and Sunday, with each session accommodating 60 participants. Parents can join their children online to learn about coral-related knowledge. The course content includes: 1. An introduction to coral, featuring the types, characteristics, and current ecological challenges faced by corals in the Northeast Coast; 2. Participants will hand-paint their own coral bases and plant corals on them themselves, contributing to coral restoration efforts. The aim of this educational initiative is to engage more people in understanding the importance of coral and marine life conservation. A coral farm has been established in the Marine Resources Restoration park for coral cultivation. It provides professional coral farming techniques and related conservation advice to the technical staff of the New Taipei City Fisheries and Fishing Ports Management Office, with the goal of preserving the coral in the Northeast Coast waters. Currently, 5,000 coral specimens are being cultivated within the park.
Sustainable Impact:NTOU implemented the "New Taipei Coral Marine Education Promotion Project", supported by the Ocean Affairs Council. The initiative offered eight weekend sessions of free "Coral School" programs for families, combining online lessons with hands-on coral restoration activities. Participants learned about coral species, ecological challenges, and conservation practices, then created and planted coral bases to support reef recovery.In parallel, a coral farm was established within the Marine Resource Restoration Park, successfully cultivating over 5,000 coral colonies. The project also provided technical training and guidance to the New Taipei Fisheries and Harbor Management Office to strengthen local restoration capacity.Through education and practical engagement, the project enhanced public environmental awareness and supported marine biodiversity conservation. It aligns with SDG 14.2.2 (protect and restore marine ecosystems) and SDG 4.3.4 (integrate environmental education for sustainable development).
承辦新北市政府113年獲得海洋委員會補助的「新北市海域珊瑚海洋教育推廣工作計畫」,每週六、日開設8梯次免費「珊瑚小學堂」活動課程,每梯次60個名額,讓家長帶著小朋友一起在線上學習珊瑚相關的知識,課程內容包含:1. 認識珊瑚課程,介紹東北角的珊瑚種類、特徵及目前面臨的生態挑戰;2. 由學員親手彩繪自己的珊瑚基座,親手在上面種植珊瑚,為珊瑚的復育盡一份心力。希望在教育推廣工作中,讓更多民眾一起參與,讓大家瞭解珊瑚及海洋生物保育的重要性。在海洋資源復育園區,設立珊瑚農場,養殖珊瑚,提供專業的珊瑚養殖技術及相關保育珊瑚的意見給新北市漁業及漁港事業管理處的技術員人,保育東北角海域的珊瑚,目前一共培育5,000株珊瑚在園區當中。
永續影響力:本校承辦新北市政府「海域珊瑚海洋教育推廣工作計畫」,透過每週末開設的八梯次「珊瑚小學堂」,以免費線上課程形式向親子族群推廣海洋生態知識與珊瑚保育觀念。課程內容包括認識東北角海域珊瑚種類、生態現況與威脅,並設計實作活動如珊瑚基座彩繪與人工珊瑚種植,讓學員親身參與復育體驗。此外,在海洋資源復育園區設立珊瑚農場,現已成功培育5,000株珊瑚,並將技術與管理經驗提供給新北市漁業及漁港事業管理處,建立地方永續復育機制。本計畫不僅提升民眾海洋保育意識與參與度,也深化環境教育與科學實踐的結合,落實 SDG 14.2.2「保護海洋生態系」及 SDG 4.3.4「推廣永續發展教育與環境素養」之精神。


Evidence:
https://www.beclass.com/rid=284d88d6652055693c26
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/859810693.pdf
8. Promotion of abalone culture industry: abalone larvae rearing and new breeds development
振興臺灣九孔養殖產業—種苗培育與不同品系研發
The National Taiwan Ocean University has successfully bred the abalone Haliotis diversicolor (108 strain) in collaboration with the Fisheries Research Institute. To continuously enhance the quantity of 108 strains, the project is engaged in conservation, intermediate rearing, and seed breeding while providing guidance and promotion to industry farmers and tracking the effectiveness of these efforts. At least 30,000 seedlings of the 108 strain, each with a shell length of over 10 mm, have been successfully cultivated and transferred to the Gong-liao aqua-center, New Taipei City, for further intermediate rearing and selection. The project has established a connection with seven abalone farmers, including four hatcheries in Tongxiao, Miaoli, and Toucheng, Yilan, as well as three growout farms in New Taipei City. One of the nurseries in Yilan has successfully obtained the 108 strains and cultivated pure and hybrid seedlings. The remaining farmers have been provided customized guidance on disease prevention, breeding techniques, and marketing promotion based on their needs. Additionally, during the project, we completed a food and agriculture education plan focusing on small abalone, aimed at promoting the transformation and management of traditional abalone farming, enhancing the value of aquatic products, and achieving sustainable development of local industries.
Sustainable Impact:NTOU, in collaboration with the Fisheries Research Institute, has continued the "Abalone 108 Line Breeding and Industry Promotion Program", focusing on genetic improvement, seed production, and sustainable aquaculture practices. Over 30,000 juvenile abalones (shell length >10 mm) of the 108 line were successfully bred and transferred to the New Taipei Marine Resource Restoration Park for intermediate cultivation.The project established seven pilot farms across Miaoli, Yilan, and New Taipei, offering tailored guidance on disease prevention, breeding optimization, and marketing strategies. One hatchery in Yilan successfully produced both purebred and hybrid offspring.Additionally, a food and agricultural education plan was designed to promote abalone culture transformation and value-added seafood development.This initiative integrates marine resource conservation, technological innovation, and local economic sustainability, aligning with SDG 14.2.2, 14.2.3, 14.3.1, and 14.3.3, emphasizing sustainable management, marine ecosystem restoration, and resilient aquaculture development.
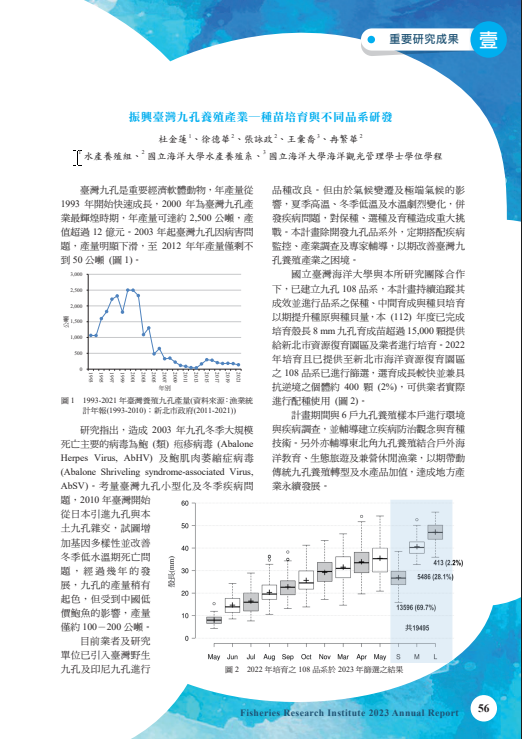
國立臺灣海洋大學與水產試驗所的研究團隊合作選育出九孔108 品系,為持續提升 九孔108 品系的種原和種貝數量,本計畫持續進行保種、中間育成與種貝培育,並進行業 者輔導及推廣,持追蹤其成效。本年度成功培育殼長10 毫米以上之九孔108 品系種苗至 少30,000 顆,並轉移至新北市資源復育園區進一步中間育成及選育。本計畫建立追蹤7 戶九孔養殖樣本戶,包括位於苗栗通霄及宜蘭頭城的4 戶種苗場和位於新北市的3 戶養 成場。其中宜蘭的一戶種苗場已取得九孔108 品系,並成功培育純品系及雜交品系種苗。 其餘樣本戶我們則依其需求分別提供疾病防治、育種技術及行銷推廣的輔導。此外,計畫 期間我們還完成了一份以九孔為主題的食農教育企畫書,旨在促進傳統九孔養殖的轉型 與經營,推動水產品加值,達成地方產業的永續發展。
永續影響力:國立臺灣海洋大學與水產試驗所共同進行「九孔108品系」育種與推廣計畫,致力於提升國產九孔的種原品質及養殖效益。本年度成功培育殼長10毫米以上種苗逾30,000顆,並移交至新北市資源復育園區進行中間育成與選育,建立穩定的繁養體系。計畫同時建立七戶養殖樣本戶,提供疾病防治、育種技術與行銷策略輔導,促進產業技術交流與升級。此外,團隊完成以九孔為主題的食農教育企畫,推廣海洋養殖與地方產業結合的永續理念,強化社區與產業鏈的連結。此計畫不僅提升海洋生物資源的永續利用與復育效能,也兼顧教育推廣與經濟價值創新,充分落實 SDG 14.2.2、14.2.3、14.3.1、14.3.3 所強調的永續海洋資源管理與產業升級目標。
Evidence:
https://www.tfrin.gov.tw/theme_data.php?theme=book_data&sub_theme=important&id=5044
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/539200718.pdf
9. Executed the "2024 Fishery Production and Marketing Groups Outsourcing Consultation and Guidance Plan"
執行「113年度漁業產銷班委外諮詢輔導計畫」
In order to strengthen the management guidance of Fishery Production and Marketing Groups, implement training on the operation and development of each Fishery Production and Marketing Groups, and increase the opportunities for mutual growth between Fishery Production and Marketing Groups. NTOU s Fisheries Extension Committee invites professional professors in various fields to go to the countryside to provide on-site consultation and guidance for Fishery Production and Marketing Groups. It is expected to improve the operational capabilities of Fishery Production and Marketing Groups, thereby strengthening the competitiveness of my country s fishery, in line with international standards, and enabling the sustainable development of fisheries.
Sustainable Impact:To strengthen the management and sustainability of Taiwan's fisheries, the Fisheries Extension Committee of National Taiwan Ocean University organized on-site consulting programs led by academic experts.Professors from various fields visited local fisheries to provide professional guidance and promote better operational practices among fishermen's production and marketing groups.The initiative enhances cooperative learning, improves productivity, and builds long-term competitiveness for the fishing industry.By integrating academic expertise into local fisheries management, this program fosters sustainable fisheries development and community resilience, aligning with SDG 14.2.2 — Strengthening fishery management and sustainable production capacity.
為強化漁業產銷班經營輔導,落實培訓各漁業產銷班經營發展,增加產銷班間相互成長之機會。由本校漁業推廣委員會,聘請各領域之專業教授,下鄉提供產銷班現場諮詢輔導,期能提升產銷班作業能力,進而強化我國漁業競爭力。
永續影響力:為強化我國漁業產銷班之經營與管理能力,國立臺灣海洋大學漁業推廣委員會組成專業輔導團隊,聘請各領域專業教授深入漁村與產區,針對漁業產銷班進行現場經營諮詢與輔導。此計畫旨在協助漁民建立完善的產銷制度,提升作業效率與經濟效益,並透過產銷班之間的經驗分享,促進互相學習與成長。透過專業知識下鄉輔導機制,不僅提升產業競爭力,更有助於漁業的永續發展與在地社區的經濟穩定,具體落實SDG 14.2.2「強化海洋資源管理與永續產業培力」之目標。


Evidence:
https://fased.fa.gov.tw/fa-Sed/jsp/login.jsp
10. fishing industry and Marine Citizen Scientist
牽罟公民科學家
Qiangou, also known as ground drag netting, was once a vital fishing activity along Yilan''s coast. Teams, primarily composed of able-bodied men from the village, would cast their nets whenever they spotted a school of fish during the fishing season. Everyone involved shared a share of the catch. This method of fishing, which involved working together to haul the nets ashore, has gradually declined. In recent years, to strengthen community development and preserve traditional culture, the port community of Toucheng, Yilan, has revived the Qiangou culture through tourism activities, allowing visitors to experience it after nearly 40 years of absence.
Sustainable Impact: The revival of the Qian-gu (shore seine) fishing tradition in Toucheng, Yilan, exemplifies the objectives of SDG 14.2.2, which emphasizes collaboration with local communities to promote sustainable management of aquatic ecosystems.
By transforming this once-declining collective fishing practice into a community-based tourism activity, the Port Community in Yilan preserves traditional maritime knowledge while promoting environmental awareness. The initiative engages local residents and visitors in participatory learning about sustainable fishing methods and marine ecosystem conservation.
Through cultural revitalization and eco-tourism, the project strengthens community identity, supports local development, and enhances understanding of the interdependence between human activity and coastal ecology—demonstrating how cultural heritage can serve as a pathway to marine sustainability.
牽罟,又稱地曳網,曾是宜蘭沿海地區重要的漁業活動。隊伍主要成員由村內壯丁組成,魚汛期間一旦發現魚群出沒即下網,凡是參與的人皆能分到一些漁獲,這種集合眾人之力,將漁網拖上岸的捕魚方式已逐漸沒落。 直到近年來,為強化社區發展、保存傳統文化,宜蘭頭城的港口社區,重新以旅遊活動的方式,帶領遊客體驗消失近40年的牽罟文化。
永續影響力:牽罟文化的重現以社區合作與文化保存為核心,符合 SDG14.2.2「與地方社區合作促進水域生態永續」的精神。宜蘭頭城港口社區透過旅遊導向的方式,復振牽罟這項傳統漁法,不僅保存地方漁業知識與文化記憶,也讓參與者理解永續漁撈與生態保育的重要性。此活動串聯社區居民、地方組織與遊客,推動海洋文化教育與永續觀光,達成文化保存與生態永續並行的目標。


Evidence:
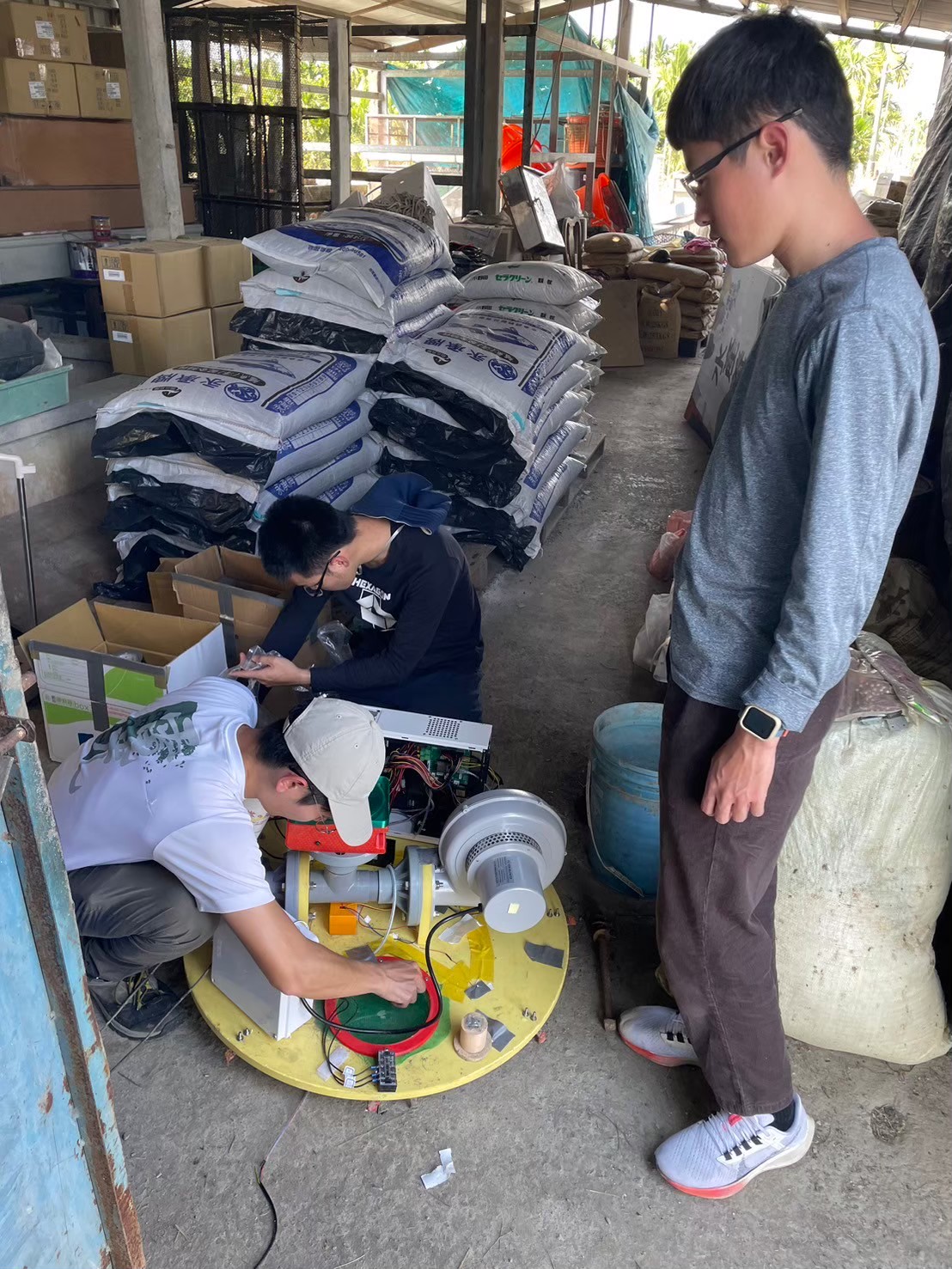
11. Intelligent Aquaculture Feeding Equipment and System Design
智慧化水產養殖投料機具及系統開發應用
Threadfin is a high-value marine food fish. According to the Taiwan Fisheries Department''s Annual Report on Fisheries Statistics 2023, the annual production of fish is approximately 13,200 tonnes, with an annual production value of NT$2.57 billion. In recent years, the aquaculture industry has faced threats such as extreme weather, depletion of near-shore fishery resources, and an aging workforce, making introducing artificial intelligence solutions in aquaculture an inevitable trend. China, South Korea, Japan, Norway, the United States, the European Union, Canada, Australia, and Taiwan primarily develop artificial or semi-automatic aquaculture technologies worldwide. Due to the high proportion of individual aquaculture farms in Taiwan, the relatively high costs of fishpond acquisition, as well as the difficulty in recruiting workers, and the lack of high-tech talent willing to take over traditional aquaculture models due to the declining birth rate, the industry''s competitiveness has been insufficient. One of the shortcomings of traditional automatic feeders is the inability to determine the remaining feed quantity and the amount of feed ejected. Therefore, our team uses a self-designed weighing module and laser ranging module to estimate the remaining feed quantity in the feed hopper and the amount of feed ejected. At the same time, the smart feeder uploads this information to a cloud database, allowing aquaculture farmers to know the actual feeding situation and establish a concrete aquaculture strategy. Considering the possibility of feed breakage affecting feeding, the smart feeder uses wind power as its power system. Since a large amount of feed will be fed in the late stage of aquaculture, there is a possibility of feed accumulating at the bottom of the feed hopper, causing blockage. Therefore, our team uses a controllable roller to create disturbances to prevent blockage and adds a device that can adjust the size of the bottom opening, allowing aquaculture farmers to adjust according to the feed size. To improve the problem that traditional automatic feeders cannot control the feeding direction, our team designed a cloud platform consisting of a main mechanism and a rotating nozzle. The main mechanism controls the rotation of the rotating nozzle, and the rotation angle is 0 to 180 degrees. There are two modes: Mode 1, back-and-forth scanning; Mode 2, specific angle projection. This mode will cooperate with water splash recognition to achieve precise feeding. The goal of this system is to promote and apply the previously established smart aquaculture system technology in land-based aquaculture farms where electricity and communication are more convenient. The previous automatic feeding system is miniaturized and lightweight, and the feed quantity and position can be adjusted according to the fish''s water splash analysis. Coupled with the communication network, it can be more easily integrated with AI aquaculture strategies and management. In addition, the aquaculture data is recorded in the form of data to promote and try to solve the operating model of aquaculture farmers.
Sustainable Impact:The development of an AI-powered smart feeding system for aquaculture aligns with SDG14.2.2, 14.3.1, and 14.3.2.
By integrating AI algorithms, weight and distance sensors, and cloud-based monitoring, the system optimizes feeding precision, minimizes feed waste, and reduces water pollution. These innovations contribute to climate adaptation, emission reduction, and sustainable resource management in the aquaculture sector.
In collaboration with local fish farmers, the project applies data-driven management to improve production efficiency and resilience to climate challenges. It promotes cleaner aquaculture practices, supports ecosystem conservation, and demonstrates how technological innovation can drive both economic viability and environmental protection. This initiative embodies a model of sustainable blue economy through academic–industry collaboration and digital transformation for marine and climate sustainability.
午仔魚為高經濟價值之海水食用魚類,根據2023年漁業署漁業統計年報資料午仔魚年產量大約1.32萬公噸,年產值約達25.7億元新台幣。近幾年水產養殖業面對極端氣候、近海漁業資源枯竭、從業人口高齡化等威脅,養殖業導入人工智慧解決方案乃大勢之所趨。世界各國之人工或半自動養殖技術,大都由中國、韓國、日本、挪威、美國、歐盟、加拿大、澳洲及臺灣提出。由於臺灣的水產養殖業個體養殖戶比例高,相對魚塭取得成本也偏高,加上少子化的影響導致現今招工不易及高科技人才鮮少願意承接傳統水產養殖模式等等因素,養殖的產業競爭力不足。 傳統的自動投料機缺點之一就是不知道剩餘飼料量與射出飼料量,因此本團隊使用自行設計的秤重模組與雷射測距模組來推算儲料桶剩餘飼料量與射出飼料量。同時智慧投餌機會把這些資訊上傳至雲端資料庫,讓養殖業者得知實際的餵食情況,好建立具體的養殖策略。考量到飼料容易破碎造成攝食情況不理想的可能,智慧投餌機使用風力作為動力系統。由於水產養殖後期會投餵大量的飼料,會有飼料堆積於儲料桶底部造成堵塞的可能,因此本團隊使用一可控滾輪造成擾動避免堵塞,同時加入可調整底部開口大小的裝置,讓養殖業者可以根據飼料大小自行調整。為了改善傳統的自動投餌機不能控制投餌方向的問題,本團隊設計了包含主要機構與旋轉噴頭兩個部分的雲台,主要機構控制旋轉噴頭轉動,旋轉角度為0到180度,有兩種模式,模式一,來回掃射;模式二,特定角度投射,此模式會配合水花辨識進而達成精準投料。 本系統的目標是在電力與通訊更加方便的陸上養殖場域下,結合以往建立的智慧養殖系統技術做推廣與應用,將之前自動射料系統加以小型化、輕量化,可依魚隻水花分析調整射控料量與位置,再搭配通訊網路,更能方便結合AI的養殖策略與管理。另外以數據的形式記錄養殖資料,推廣並試圖解決養殖業者問題的經營模式。
永續影響力:本團隊開發智慧投餌系統,結合 AI 與感測技術以改善傳統養殖效率,符合 SDG14.2.2、14.3.1、14.3.2 之永續指標。此系統透過數據化管理、雲端監控與精準投餌,降低飼料浪費與水體污染,促進減碳與氣候調適。同時藉與地方養殖業者合作推廣智慧化生產,提升產業韌性與海洋環境永續。此研究兼具技術創新、教育推廣與環境保護效益,展現產學合作落實藍色經濟與低碳永續之具體實踐。

Evidence:
https://tie.twtm.com.tw/zh-tw/exhibition-detail/4777?utm_source
12. fishing industry and Marine Citizen Scientist
漁業公民科學家
The goal of this initiative is to ensure the sustainable use of fishery resources in the Si Hu and Kou Hu regions of Yunlin, the conservation of coastal marine ecosystems, and the sustainability of fishing villages and small-scale fisheries, in alignment with SDG 14 targets. The main objective is to incorporate the concept of sustainable use of fishery resources and responsible fishing practices, combining the application of natural and social sciences to transform fishery management policies into localized measures. Through the foundation of citizen science, a fisheries management mechanism based on input and output is established, fostering the proactive capabilities of marine citizens and promoting the local implementation of responsible fisheries. This initiative has been in progress for over two years, during which, in the 113th year, it assisted the Yunlin County Offshore Fishing Vessel Association and the Fishermen's Rights and Environmental Sustainability Center to obtain the Ocean Conservation Administration's "Environmental Fleet" project. This includes monitoring and surveying marine debris, citizen scientist surveys of the longfin mako shark, and the establishment of a dolphin-friendly fishing fleet demonstration area. Five citizen scientists were trained, expanding the future possibilities of sustainable development through the participation of frontline fishery users in responsible fisheries, enhancing the sustainable development of fisheries in the Si Hu and Kou Hu regions. Additionally, teachers and students from our school, along with students from Beigang Agricultural and Industrial School and members of the Association, jointly conducted tagging and release of longfin mako sharks and marine citizen scientists collected firsthand data on marine debris and fish catches. Through training and workshops, a consensus was formed, becoming an exemplary model for establishing responsible fisheries along the coast. The initiative will continue to promote citizen scientist activities to enhance fishermen's sense of identity with their place of residence, to promote sustainable conservation and concurrent fishing industries, with the hope of establishing the Si Hu and Kou Hu regions of Yunlin as a unique sustainable demonstration fishing village in our country.
Sustainable Impact: National Taiwan Ocean University has implemented a long-term project in Yunlin’s Sihu and Kouhu coastal regions to promote sustainable fisheries through civic science and responsible fishing practices. The initiative integrates natural and social sciences to localize fisheries management policies, enhance community awareness, and establish citizen participation mechanisms for responsible fisheries.
In 2024, the university supported local fishery associations in obtaining the Ocean Conservation Administration’s “Eco-Fleet” program, which includes marine waste monitoring, shark tagging, and dolphin-friendly fishing demonstrations. Five citizen scientists were trained to engage in marine data collection and sustainable fishing practices.
This initiative aligns with SDG 14.2.2 – Sustainable Fisheries (Community Service), emphasizing educational outreach and community engagement in the sustainable management of fisheries and aquaculture. Through these efforts, NTOU demonstrates its leadership in combining science, education, and social responsibility to advance marine conservation and sustainable coastal livelihoods.
環境永續中心獲得海保署「環保艦隊」計畫,包括海上廢棄物監測與調查、龍紋鯊公民科學家調查及白海豚艦隊漁業友善示範區。並培育5位公民科學家,藉由第一線漁業使用者對於責任制漁業之投入參與,擴大永續發展的未來可能性,增進四湖口湖地區之永續漁業發展。另外本校師生與北港農工學生及協進會成員共同進行龍紋鯊標識放流及海洋公民科學家蒐集第一手海廢與漁獲資料,藉由培訓與講習營凝聚共識,成為建立沿近海責任制漁業最佳示範。 後續將持續推動公民科學家活動,以提高漁民對於居住地之認同感,以推動永續保育並行捕撈漁業,期望將雲林四湖、口湖地區建置為我國獨具在地特色之永續示範漁村。
永續影響力:國立臺灣海洋大學長期推動雲林四湖、口湖地區的永續漁業發展,結合公民科學與責任制捕撈觀念,推廣在地化的漁業管理模式。活動聚焦於漁業資源永續利用、海洋生態保全及小規模家計型漁業之永續經營,協助地方建立海洋公民自覺與責任制漁業實踐。113年度協助地方漁民團體獲得海保署「環保艦隊」計畫,並培育公民科學家推動漁業監測與資料蒐集。此舉符合 SDG14.2.2 可持續漁業(社區服務) 指標精神,展現大學以教育與科學行動支持在地社區落實永續漁業與海洋保育。
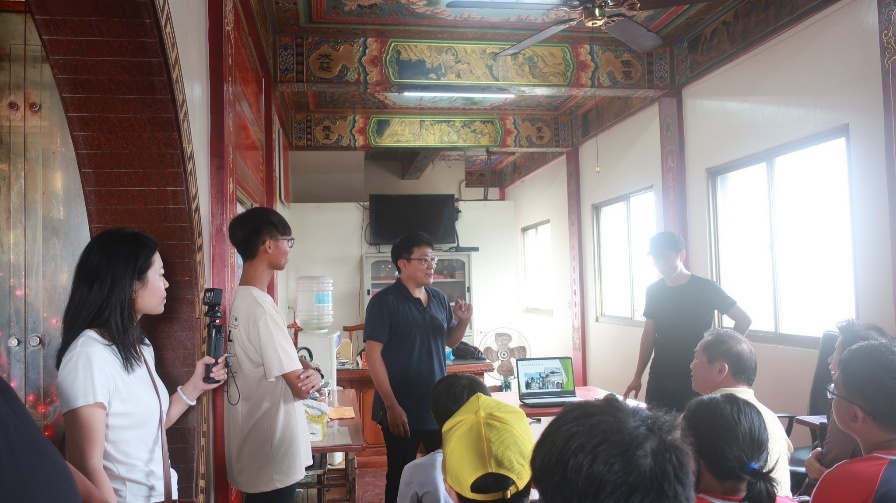
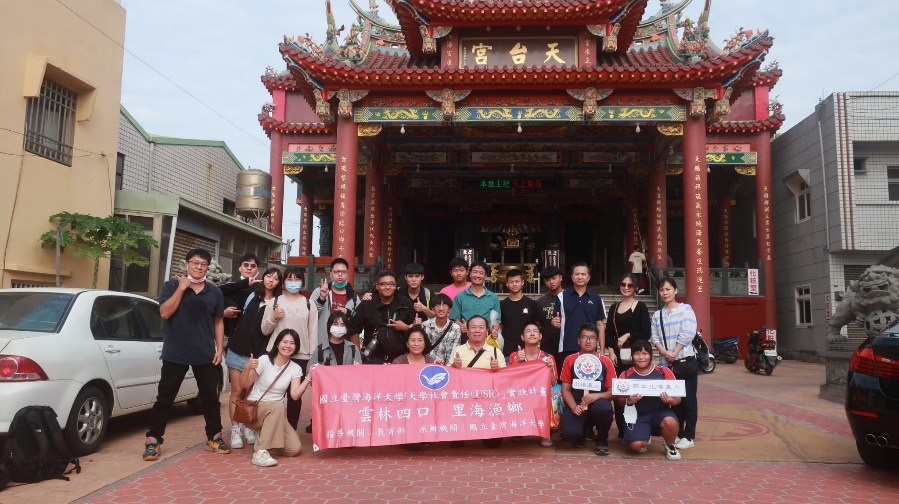


Evidence:
https://ctl.ntou.edu.tw/p/412-1105-12210.php
13. International Conference on the Impact and Adaptation of Climate Change on Fisheries
漁業面對氣候變遷之衝擊與調適國際研討會
Climate change has become a global issue, posing severe challenges to nations around the world. To address these challenges, the National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU) held the “International Symposium on the Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries and Adaptation” on October 15–16 at the National Museum of Marine Science and Technology. This symposium was organized by the Institute of Marine Affairs and Resource Management (IMARM) as a special event celebrating NTOU's 71st anniversary. The conference brought together experts and scholars from Canada, Japan, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Taiwan, attracting nearly a hundred participants. The attendees discussed global challenges and adaptation strategies faced by the fisheries sector under climate change, aiming to promote the sustainable development of fisheries worldwide. Taiwan plays a key role in global fisheries, particularly in the Pacific longline industry targeting bigeye, yellowfin, and albacore tunas. Taiwan's distant-water squid jigging fleet also targets saury and holds a significant competitive edge internationally—since 2013, Taiwan has led global catches of Pacific saury in the North Pacific. During his opening remarks, NTOU Vice President Dr. Ming-An Lee highlighted that not only distant-water fisheries but also coastal fisheries are increasingly affected by climate change, emphasizing the importance of adaptive management policies. He also noted that Taiwan's Climate Change Response Act, revised in 2023, sets a national goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, underscoring new challenges and responsibilities for fisheries management and climate adaptation. The symposium featured several distinguished speakers, including: Prof. William Cheung, a leading expert on climate modeling from the University of British Columbia, who shared insights on sustainable fisheries through modeling approaches that integrate stakeholder perspectives. Prof. Nobuyuki Yagi from the University of Tokyo, who discussed the impacts of climate change on Japan's fisheries and the potential of seaweed in mitigating methane emissions. Dr. Encarnacion Emilia S. Yap, Vice Chancellor of the University of the Philippines Visayas, who presented strategies for reducing the risks and vulnerabilities of the Philippine fisheries sector under climate change. Mr. Jun-Yang Huang, Director of the Ocean Policy Research Institute at the Sasakawa Peace Foundation (Japan), who introduced Japan's response to the impacts of climate change on squid fisheries through the development of cold-chain logistics systems. The symposium also featured Dr. Muhamad Naimullah, Assistant Professor at Universiti Malaysia Terengganu and an alumnus of NTOU, who presented research on how ENSO (El Niño–Southern Oscillation) events influence Taiwan's swimming crab fishery. Taiwanese experts further shared studies on the impacts of climate change and corresponding adaptation strategies for eel, squid, mackerel, and other fishery resources in the southwestern Taiwan waters. The symposium was initiated by Distinguished Professor Kwang-Ming Liu, Director of IMARM**, who expressed gratitude to the Ministry of Agriculture for its funding support, which made this international symposium possible. The event showcased Taiwan's achievements in climate change response and adaptation in the fisheries sector. The project was jointly conducted by six professors with diverse expertise, including Professors Kwang-Ming Liu, Chih-Shin Chen, Ting-Chun Kuo, and Wen-Ning Chang of NTOU; Prof. Kuo-Wei Lan from the Department of Environmental Biology and Fisheries Science, NTOU; and Prof. Wen-Bin Huang from National Dong Hwa University. Together, they assessed the impacts of climate change on Pacific tropical and temperate tunas, sharks, saury, and Argentine squid, using modeling approaches to project habitat shifts and changes in fishery yields under various climate scenarios.
Sustainable Impact: National Taiwan Ocean University hosted the International Conference on the Impact and Adaptation of Fisheries to Climate Change in October 2024, aligning with SDG14.2.2, 14.2.3, 14.4.1, 14.4.2.
The event brought together experts from Canada, Japan, Malaysia, and the Philippines to exchange insights on climate-induced challenges in fisheries and adaptation strategies. Discussions covered topics including low-carbon energy use, climate education, sustainable fishery management, marine pollution reduction, and international cooperation in capacity building.
By integrating science-based climate analysis with community-focused sustainability practices, the conference demonstrated higher education’s vital role in promoting global collaboration on climate action and sustainable oceans. It not only advanced regional understanding of climate resilience in marine sectors but also strengthened academic networks supporting the transition toward carbon neutrality and responsible ocean governance.
氣候變遷已成為全球性課題,各國皆面臨嚴峻的挑戰,國立臺灣海洋大學於10月15至16日假國立海洋科技博物館舉行「漁業面對氣候變遷之衝擊與調適國際研討會」,本次研討會為海洋事務與資源管理研究所為海大71週年校慶特別舉辦。研討會匯聚來自加拿大、日本、馬來西亞、菲律賓等各國的專家與國內學者,近百位參與者,共同探討全球漁業面對氣候變遷的挑戰與應對策略,並進一步推動漁業永續發展。 臺灣在全球漁業中具有關鍵地位,包括太平洋延繩釣漁船的主要漁獲,如大目鮪、黃鰭鮪與長鰭鮪,遠洋魷釣船還能兼補秋刀魚,在國際上也有占有相當優勢,自2013年以來臺灣在北太平洋秋刀魚捕撈中更是全球領先。海大李明安副校長於開幕致詞時表示,不僅是遠洋漁業,沿岸漁業資源同樣受到氣候變遷的影響,凸顯了應對氣候變遷調適政策的重要性。臺灣於去年修訂《氣候變遷因應法》,明定我國應在2050年達成溫室氣體淨零排放,這不僅是國家層級的承諾,也對漁業管理和應對氣候變遷提出了新的要求。 此次會議邀請到氣候變遷模式的權威英屬哥倫比亞大學William Cheung教授分享在永續漁業重要見解與經驗,包含最新的模式並結合各利害關係人的觀點;日本東京大學Nobuyuki Yagi教授分享日本漁業受到氣候變遷所造成的這種影響,以及海藻減緩甲烷排放的潛力;菲律賓大學米沙鄢分校Encarnacion Emilia S. Yap副校長也分享了減少菲律賓漁業部門面對氣候變遷的風險與脆弱性的經驗;日本笹川平和財團海洋政策研究所黄俊揚主任則分享日本魷魚漁業在受到氣候變遷衝擊,轉而發展冷鏈物流的應對與調適。 另外,臺灣沿近海漁業也邀請到過去曾來臺求學的馬來西亞登嘉樓大學Muhamad Naimullah助理教授分享臺灣梭子蟹受聖嬰–南方震盪(ENSO)事件之影響,國內專家並針對鰻魚、小卷、鯖魚、臺灣西南海域漁業資源受到氣候變遷的影響及因應措施。本次研討會的發起人海資所所長劉光明特聘教授感謝農業部的補助計畫,讓本次國際研討會成功舉辦,展現我國在氣候變遷的因應與調適成果。此計畫由六位不同專長領域的老師,包含海大海資所劉光明教授、陳志炘教授、郭庭君副教授、張文寧助理教授、環漁系藍國瑋教授及東華大學黃文彬教授,共同針對我國太平洋熱帶鮪類、溫帶鮪類、鯊魚、秋刀魚與西南大西洋阿根廷魷受氣候變遷影響,建構模擬推估棲息地之移動,以及漁獲量的變動。
永續影響力:國立臺灣海洋大學於2024年舉辦「漁業面對氣候變遷之衝擊與調適國際研討會」,邀集加拿大、日本、馬來西亞、菲律賓等國專家學者,共同探討氣候變遷對漁業的影響及永續對策,符合 SDG14.2.2、14.2.3、14.4.1、14.4.2之精神。研討會整合低碳能源議題、氣候教育推廣、永續漁業政策及塑膠減量行動,並促進跨國研究交流與專業能力培育。此舉展現學校以國際合作推動氣候行動與海洋永續之具體實踐。
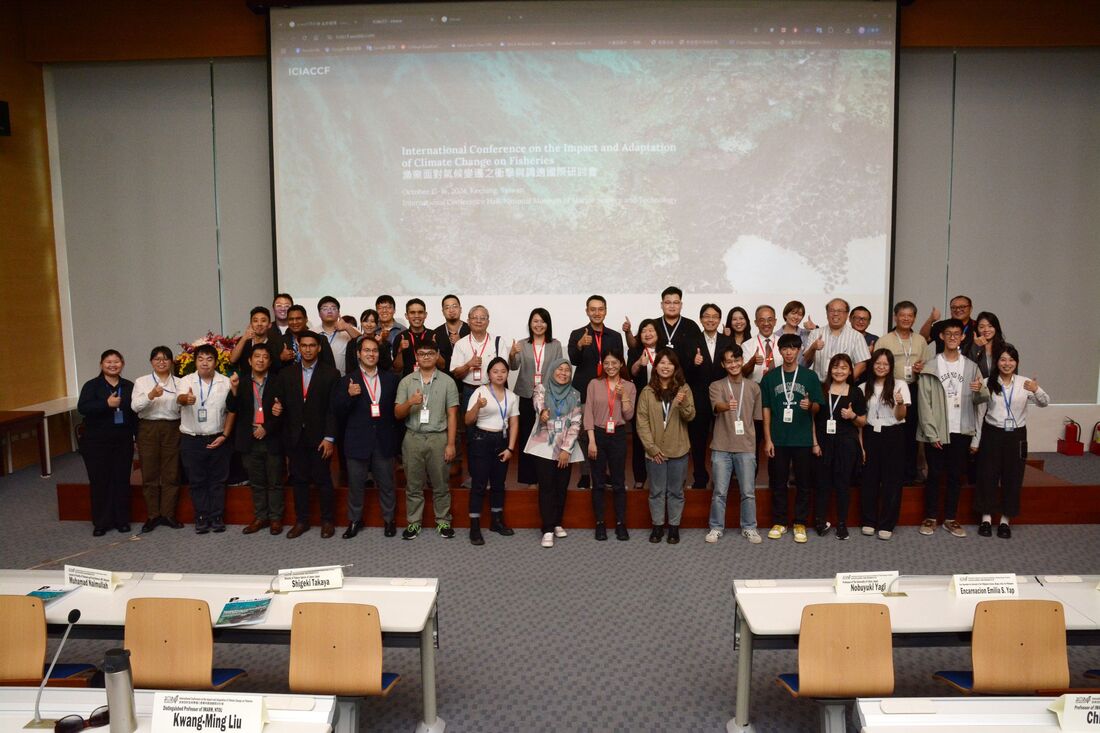


Evidence:
14. Investigation on aquaculture carbon sink and establishment of measurement methodology
養殖漁業碳匯調查及建立量測方法學研究
Due to the absence of a matching Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) mechanism in our country, the national greenhouse gas emissions inventory has yet to establish wetland-related carbon sink data. In order to understand the overall carbon sink variations and potential reductions in emissions in our country, as well as to adhere to the three core principles (measurable, verifiable, and reportable) and five key characteristics (additivity, conservatism, permanence, avoidance of harm, and avoidance of double counting) required for future voluntary reduction projects, this project will focus on carbon sinks in aquaculture, including the milkfish and sea bass farming industries. We will measure the greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sinks in water bodies and sediments, and analyze their local coefficients. The goal is to accurately estimate the carbon sink or carbon source capabilities of wetlands in line with the international trend towards net-zero emissions and to achieve the domestic net-zero emissions policy objectives.
Sustainable Impact: This project addresses the current gap in Taiwan’s national greenhouse gas inventory, which lacks wetland carbon sequestration data. It focuses on measuring greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in milkfish and seabass aquaculture systems, including both water and sediment compartments, to establish localized carbon coefficients. The study supports the development of Taiwan’s Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) framework and aligns with the three key MRV principles—measurability, verifiability, and reportability—as well as the five essential attributes of carbon management: additionality, conservativeness, permanence, avoidance of leakage, and prevention of double counting.
The outcomes will enhance national understanding of wetland carbon fluxes, inform voluntary mitigation programs, and contribute to net-zero strategies under SDG 13.3–13.4. Simultaneously, the research advances sustainable aquaculture and coastal wetland carbon management, aligning with SDG 14.2–14.3. By quantifying blue carbon potential and integrating it into national climate policy, this project builds a scientific foundation for low-carbon aquaculture and climate-resilient marine ecosystems in Taiwan.
因我國尚未建立相符之監測、報告與驗證機制(MRV),國家溫室氣體排放清冊尚未建立濕地相關碳匯量數據,為了解我國整體之碳匯變動量及可減少之排放量,以及未來自願減量專案中所需之三大原則(可量測、可驗證、可報告)和五大特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免產生危害及避免重複計算),本案將針對養殖漁業碳匯,包含虱目魚及鱸魚養殖產業,進行水體及底土之溫室氣體與碳匯量測,並分析其本土係數,期望可精確的推估濕地的碳匯或碳源能力,以符合國際淨零排放趨勢及達到國內淨零排放政策目標。
永續影響力:本計畫針對我國尚未納入國家溫室氣體清冊之「濕地碳匯」議題,進行養殖漁業(虱目魚與鱸魚產業)水體與底土之溫室氣體排放與碳匯量測,建立本土化碳吸存係數,補足我國MRV(監測、報告、驗證)機制缺口。研究結果將有助於掌握濕地碳源與碳匯變動,為自願減量專案奠定基礎,符合「可量測、可驗證、可報告」三原則及五項碳管理特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免危害、避免重複計算)。 此研究不僅支援國家淨零排放政策與氣候治理(SDG13.3.1–13.4.1),亦促進海岸與養殖濕地的生態碳匯功能理解(SDG14.2.1–14.3.3),為台灣藍碳管理與低碳漁業發展提供重要實證依據。
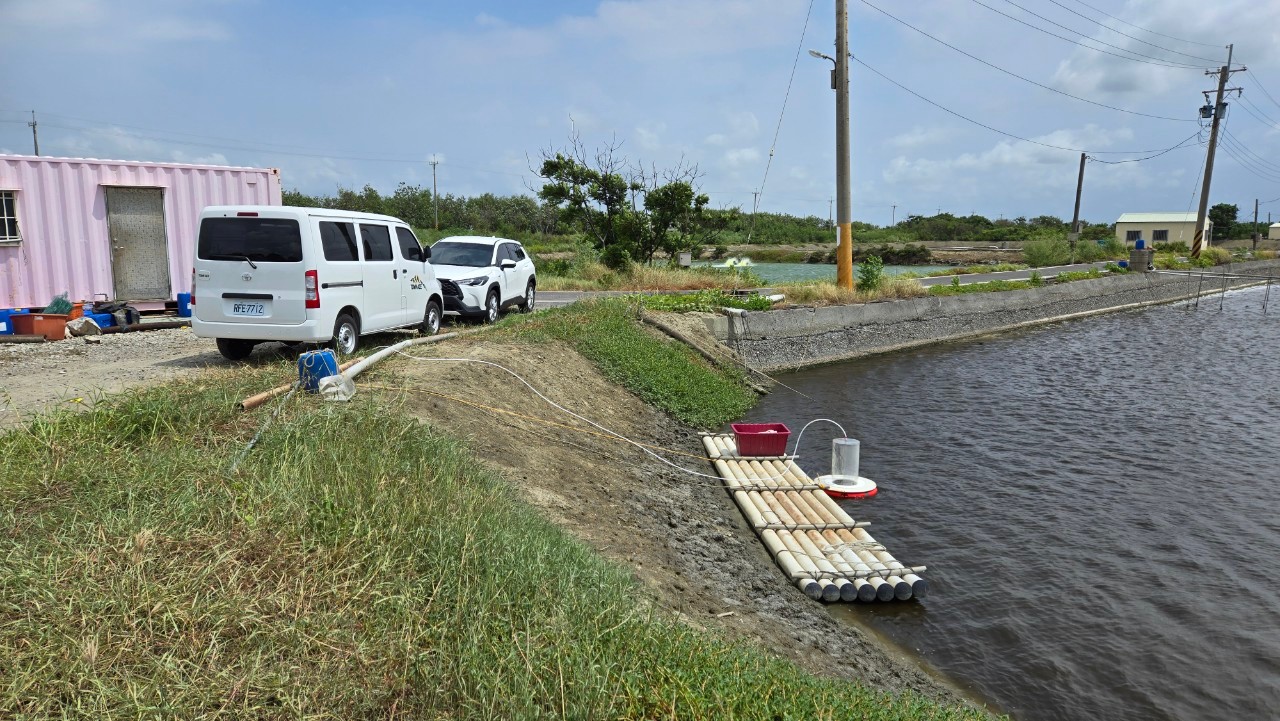


Evidence:
https://mprp.ntou.edu.tw/p/404-1017-108824.php?Lang=zh-tw&utm_source
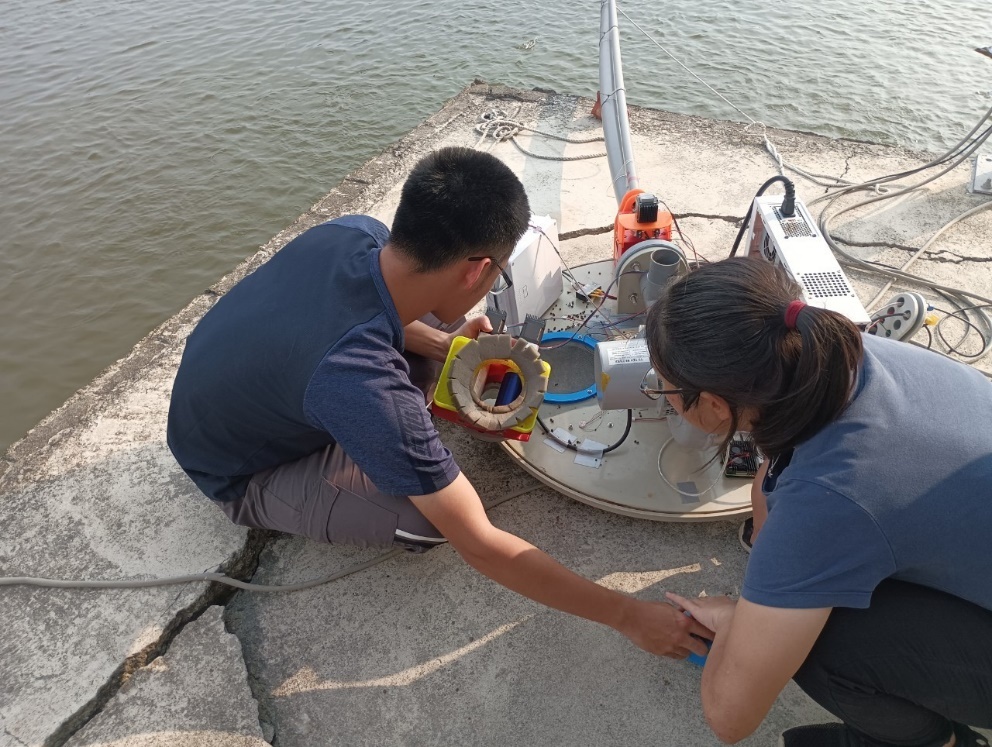
15. One-stop larval cultivation plan for lobster and fan lobster
龍蝦與扇蝦幼苗一站式培育計畫
Lobster and fan lobster are aquatic products with high economic value. After the lobster is hatched from the egg, it will go through the planktonic phyllosoma stage for more than six months, then become a sinking puerulus, and then grow into an adult shrimp. However, global climate change and overfishing have led to a sharp decline in puerulus, making it difficult to obtain seedlings and making subsequent lobster breeding more difficult. Therefore, Indonesia, the world's largest catcher of puerulus, banned the export of seedlings in 2015, making it difficult to obtain seedlings and even more difficult for further lobster raising. Our team completed the following important achievements last year: (1) Completed the technology and on-site verification of artificial seedling cultivation; (2) Produced artificial feed packages for phyllosoma seedlings, and was able to reach at least 6 monthly storage and transportation tests; (3) Complete the design of 0.5-ton mass-production breeding equipment; (4) Complete the basic formula of artificial raising feed, with a two-month survival rate of 100%; (5) Accurately determine the gonad maturity stage of broodstock and establish artificial hatching technology. In addition, we have also obtained three Taiwan patents and established a business secret protection system. The expansion of artificial seedling production and the on-site verification of the use of artificial feed are the most important tasks before enter industry. Thus, we propose this project, hoping to optimize and expand the number of artificial seedlings cultivation, basing on the previous results and combined with existing technology to carry out trial production of artificial feed to stabilize quality and reduce costs. Artificial seedlings with artificial feed will be verified in Taiwan for the whole cycle, and at the same time. In addition, the artificial ripening feed and artificial incubation technology will also begin to develop. In this way, by combining seedlings, feed, broodstocks, equipment and technical services, we will become the only one-stop industrial chain provider of lobster seedlings in the world, moreover, to create a win-win situation for marine sustainability and industrial development.
Sustainable Impact: This project addresses the critical decline of lobster and slipper lobster larvae caused by climate change and overfishing by developing a complete artificial breeding and rearing technology chain. The team successfully achieved key milestones: artificial larval cultivation, long-term storable formulated feed for phyllosoma larvae, scalable 0.5-ton production systems, and 100% two-month survival rates with formulated grow-out feed. In addition, patents and trade-secret protections were established to support commercialization.
By enabling artificial seed production and sustainable feed systems, the project reduces dependence on wild-caught glass-stage larvae, alleviates ecological pressure, and ensures the continuity of high-value crustacean resources. It advances sustainable aquaculture practices and strengthens industry resilience through innovation and circular resource use. The research directly supports SDG 14.2.2, promoting the conservation and sustainable utilization of marine resources through scientific restoration, technological innovation, and responsible aquaculture management, contributing to both ocean sustainability and blue economy growth.
龍蝦與扇蝦是高經濟價值的水產品。龍、扇蝦由卵孵化後會經過六個月以上的浮游性葉狀幼苗期,然後變成沈底性玻璃幼苗,再成長為成蝦。但是因全球氣候變遷以及過度捕撈導致玻璃幼苗的銳減,幼苗取得不易,後續更難進行龍蝦育成養殖。本團隊經前期的研究,完成下列幾個重要成果:(1) 完成人工幼苗培育之技術;(2) 製作葉狀苗人工飼料包,並能達到至少6個月保存與通過運送測試;(3) 完成0.5噸量產式培育設備設計;(4) 完成育成型人工飼料基本配方,兩個月的存活率達100%;(5) 精準判斷種蝦性腺成熟階段,建立人工孵化技術。此外,我們也獲得三項中華民國專利,建立了營業秘密保護機制。而人工幼苗擴大生產以及使用人工育成型飼料養成的現場驗證,是商業化前最重要的工作,因此我們提出本計畫,希望能根基於前期成果,結合現有資源技術,除了持續優化並擴大人工幼苗培育數量外,將進行育成型人工飼料試量產以穩定品質並降低成本。以人工苗搭配人工飼料於臺灣完成全季度測試,同時投入催熟型飼料的研發以完整龍蝦全人工孵化技術。如此,結合幼苗、飼料、種蝦、設備與技術服務,我們將成為全球唯一龍蝦幼苗一站式產業鏈提供者,為海洋永續與產業發展共創雙贏的局面。
永續影響力:本計畫針對氣候變遷與過度捕撈導致龍蝦、扇蝦幼苗數量銳減的問題,成功建立人工繁殖與育苗技術,包含人工孵化、葉狀苗人工飼料研製、量產設備設計與長期培育流程,實現全人工孵化與育成關鍵技術鏈。計畫成果能穩定供應種苗、降低野外捕撈壓力、維持海洋生態平衡,並推動高經濟價值甲殼類之永續養殖。此創新技術體系同時強化漁業自主性與產業競爭力,符合 SDG14.2.2 所倡導的「發展永續漁業與復育海洋資源」目標,為海洋保育與藍色經濟的協同發展提供典範。


Evidence:
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/740025527.pdf
16. Strategies for Promoting Sustainable Actions through the Exploration of Social-Ecological Knowledge in Kouhu, Yunlin under Environmental Change
環境變遷下雲林口湖社會生態知識探索帶動永續行動之策略
Kouhu Township, situated on the western coast of Yunlin County, represents the southernmost coastal region of the county. This area boasts diverse wetland ecosystems, including sandbars and lagoons. The majority of its residents depend on aquaculture or coastal fisheries-related industries for their livelihoods, making it a quintessential example of Taiwan's traditional fishing villages. However, in recent years, the community has faced threats and challenges to its fisheries, agriculture, community development, tourism, and industrial operations due to environmental impacts such as extreme weather events, coastal geomorphological changes, and human activities. This study centers on the "Strategies for Promoting Sustainable Actions through the Exploration of Social-Ecological Knowledge in Kouhu, Yunlin under Environmental Change." It adopts the concept of translating knowledge into industry practices, encompassing three dimensions: policy governance, industrial society, and environmental ecology. Additionally, it extends to benefit analysis of governance involving stakeholders in environmental ecology, providing strategies for local adaptation behaviors and sustainable development.
Sustainable Impact: This research, titled “Exploring Socio-Ecological Knowledge and Sustainable Actions in Yunlin Kouhu under Environmental Change,” investigates the impacts of climate change, coastal geomorphological shifts, and human activities on the socio-economic and ecological systems of Taiwan’s traditional coastal fishing villages.
By integrating three key dimensions—policy governance, socio-industrial adaptation, and ecological sustainability—the project applies local ecological knowledge to develop actionable strategies for resilience and sustainable coastal management. It also evaluates the governance effectiveness among environmental stakeholders to guide future adaptive behavior and sustainability planning.
Through interdisciplinary collaboration and community engagement, this initiative enhances the integration of science, local wisdom, and policy, aligning with SDG 14.2.2. The project serves as a model for balancing fisheries revitalization, ecological restoration, and community development in response to climate and environmental challenges.
雲林縣口湖鄉位於西部濱海,屬雲林縣最南沿海的地區,具備沙洲、潟湖等多樣濕地生態系,多數居民依賴水產養殖或沿近海漁業相關產業為生,是臺灣傳統漁村的代表之一,而近年受極端氣候、海岸地形變遷及人為活動等環境影響,對當地的漁業、農業、社區發展、觀光及產業經營皆造成威脅及衝擊。本研究以「環境變遷下雲林口湖社會生態知識探索帶動永續行動之策略」為主軸,以知識落實到產業的概念,涵蓋政策治理面、產業社會面及環境生態面等三面向,並延伸對環境生態利益關係人治理進行效益分析,提供當地進行調適行為及永續發展策略。
永續影響力:本研究以「環境變遷下雲林口湖社會生態知識探索帶動永續行動之策略」為主軸,針對極端氣候、海岸變遷及人為活動對沿海漁村生計與生態的衝擊進行分析。研究結合政策治理、產業社會及環境生態三面向,整合地方知識與產業經驗,提出具體之調適與永續發展策略,協助社區發展兼顧漁業復育與產業永續。此計畫強化地方生態知識在政策與實務間的轉化應用,促進公民參與與多方協作,實踐 SDG14.2.2 所倡導的目標,為漁村永續經營與海岸治理提供具在地性的典範。
Evidence:
https://research.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/21/1021/img/733589579.pdf
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/680271306.pdf
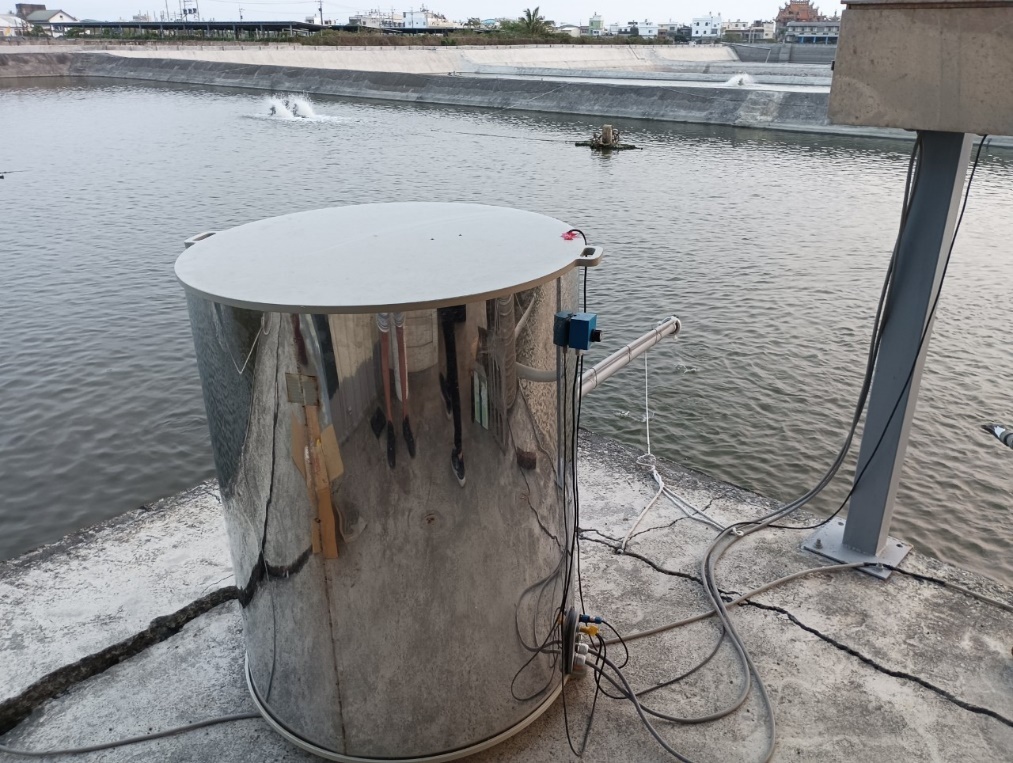
17. Precision Aquaculture Environmental Detection with Artificial Intelligence Manufacturing Decision Syste, and Intelligent /feeding Management Sy
鱸魚精準餵食及養殖環境監測與智能生產決策系統研究與開發
The sea bass farming industry in Taiwan, with over 40 years of history, is a crucial sector in large-scale aquaculture. However, it currently faces significant challenges, including an aging workforce, labor shortages, and difficulties in transferring expertise due to a lack of scientific management. To enhance IoT technology development in Taiwan's aquaculture and improve disaster response capabilities, this project focuses on transforming Taiwan's sea bass industry. It aims to integrate sensor technology, 5G communication, and IoT advancements to create a ""Sea Bass Farming Environmental Monitoring and Intelligent Production Decision-Making System,"" addressing the industry''s challenges in establishing and transferring expertise. Furthermore, by incorporating image recognition, IoT, 5G communication, and aquaculture technology, we aim to develop an ""Intelligent Precision Feeding System."" This system will help mitigate labor shortages and the inefficiencies caused by traditional equipment, which can lead to waste and water quality deterioration due to untimely adjustments. These systems will be implemented at a demonstration site for in-pond research, systematically collecting environmental and feeding data to improve real-time risk alerts, assessment, decision-making, and management efficiency in sea bass farming. This research seeks to resolve long-standing issues in Taiwan''s sea bass sector, including a lack of scientific management, limited intelligent solutions, passive risk management, labor shortages, and the rising costs of raw materials worldwide. Our goal is to propel Taiwan''s sea bass industry toward automation, digitalization, and intelligent transformation. For this year, the objectives are to further refine the precision feeding system based on the R&D foundation of 2023 and expand the demonstration of the “Sea Bass Farming Environmental Monitoring and Intelligent Production Decision-Making System” to one site. System enhancements include improving 3D printed materials for the feeding and spray modules, strengthening the remote control and communication interfaces of the feeding machine, refining the intelligent feeding and splash analysis system for varied weather and site conditions, integrating feeding logs with the environmental monitoring and production decision system, and completing cost-benefit analyses of the system's setup and usage.
Sustainable Impact: This project focuses on advancing Taiwan’s sea bass aquaculture industry through the integration of IoT, 5G communication, and image recognition technologies. It develops two major systems—an environmental monitoring and intelligent production decision platform and an AI-based precision feeding system—to address challenges such as labor shortages, inefficient management, and environmental degradation. The systems enable real-time environmental data collection, disaster response, and optimized feeding strategies, reducing waste and improving water quality.
By promoting digitalization, automation, and intelligent management in aquaculture, the research enhances the resilience and sustainability of marine resource use. It contributes directly to SDG 14.2.2 — Research supporting sustainable management and restoration of marine ecosystems, demonstrating the university’s leadership in developing smart technologies for sustainable fisheries and the blue economy
鱸魚養殖在臺灣有超過四十年歷史,被視為一項極為重要的大宗養殖產業。然而,目前我國鱸魚養殖業面臨著許多挑戰,包括人口老化、勞動力不足以及缺乏科學化管理導致經驗傳承困難。為了強化我國水產養殖業的物聯網科技發展並提高防災應變能力,本計畫以臺灣鱸魚養殖業為推動養殖漁業轉型的目標。整合包括感測器技術、5G通訊技術以及物聯網技術開發「鱸魚養殖環境監測與智能生產決策系統」改善經驗建立與傳承困難的產業困境;整合影像辨識技術、物聯網技術、5G通訊技術以及水產養殖技術開發「智能精準餵食系統」改善現有勞動力不足以及傳統設備無法適時調整造成浪費與水質惡化的痛點。相關系統擬落地於示範場址上進行池間研究,利用科學化的方式收集環境資料和進食數據,以提高鱸魚養殖業的風險即時預警、判斷和決策處理能力,以及養殖管理的效率。本研究的目標是改善臺灣鱸魚養殖業長期以來所面臨的問題,包括缺乏科學化管理、缺乏智能化解決方案、被動式的風險管理、勞動力資源的限制以及原物料上漲的世界局勢下更節省成本的管理挑戰。我們希望推動臺灣鱸魚養殖業向自動化、數位化和智能化的方向轉型發展。本年度目標為基於112年的研發基礎進一步精進鱸魚精準餵食系統並擴散鱸魚養殖環境監測與智能生產決策系統示範場域1處,系統精進方面分別完成了包括精準餵食系統進料與噴料模組3D印件材料改良、精準餵食系統投料機遠端控制與通訊介面強化、精準餵食系統智能投餵水花分析系統在不同天候、場域調適精進、精準餵食系統飼料投餵日誌資訊介接養殖環境監測與智能生產決策系統及完成完成精準餵食系統建置成本及使用效益分析等。
永續影響力:本研究以臺灣鱸魚養殖業為對象,運用物聯網、5G通訊與影像辨識技術,開發「鱸魚養殖環境監測與智能生產決策系統」及「智能精準餵食系統」,以改善人力短缺與管理效率問題。系統能即時蒐集與分析養殖環境資料,提供風險預警與決策支援,有效降低飼料浪費與水質惡化,並提升產業防災應變能力。此研究推動水產養殖向數位化、智能化轉型,實現低碳、高效與永續的漁業發展,直接符合 SDG 14.2.2(支持海洋生態系統永續管理與復原力的研究) 指標,展現大學在永續漁業與智慧藍色經濟領域的科研貢獻。


Evidence:
https://www.ardswc.gov.tw/Home/News/news_more?id=09f94c3f34ba491c89c9f1fb97a5718b
https://usr.ntou.edu.tw/var/file/90/1090/img/1658/707288676.pdf
18. The course and experiment of "Ocean Current" 『洋流學』教學與課後實驗
‘Ocean Current' after-class experiments are highly aligned with SDG 4, "Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all". Through contextualized, inquiry-based hands-on activities, students not only "see"science but also"learn by doing"and"learn by applying."Across the full workflow—design, operation, data collection, and interpretation—they cultivate critical thinking, problem-solving, and cross-disciplinary integration skills, all core competencies of quality education. The experiments adopt scalable difficulty levels and differentiated tasks to accommodate diverse prior knowledge, encouraging active participation, collaboration, and reflective feedback. In turn, these features spark curiosity about science and strengthen self-directed learning and motivation for lifelong learning. Furthermore, the'Ocean Current' course directly supports SDG 14,"Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources," by linking education and research. By understanding the physical mechanisms and biogeochemical effects of ocean currents, students can translate observations and analyses into insight and action on real-world issues, for example: • Sustainable fisheries management: Use current-driven habitat shifts, upwelling, and frontal positions to estimate the spatiotemporal distribution of fishing grounds, informing adaptive fishing effort and resource assessments. • Marine pollution response: Apply flow fields and dispersion models to understand transport pathways of floating pollutants (e.g., plastic fragments, oil spills), proposing more effective early-warning and cleanup strategies. • Habitat and protected-area planning: Use in-situ observations and remote sensing to identify ecological hotspots, migratory corridors, and high-productivity zones, thereby strengthening the scientific basis for Marine Protected Areas or managed zones. This education–research–governance linkage exposes students to evidence-based decision-making during their learning process, helping them see how science becomes public good—and later translate it into policy recommendations, public communication, and local practice in their careers. Ultimately, students will respond to global environmental challenges with scientific literacy and advance the sustainable use of marine resources with civic literacy, jointly driving the realization of SDG 4 and SDG 14.
Sustainable Impact:The"Ocean Currents"course integrates inquiry-based and experiential learning, enabling students to develop critical thinking and interdisciplinary problem-solving skills, aligning with SDG 4.1.1's emphasis on quality and inclusive education. Its participatory and reflective design promotes self-directed, lifelong learning, consistent with SDG 4.3.2, which values public and lifelong learning activities. Moreover, by linking physical oceanography to real-world applications such as fisheries management, pollution control, and habitat protection, the course directly supports SDG 14.2.2's objective of conserving and sustainably using marine ecosystems. It exemplifies how higher education can connect scientific research with societal action to advance sustainability and evidence-based decision-making.
『洋流學』的課後實驗與 SDG 4「確保包容與公平的優質教育,促進全民終身學習機會」高度契合。透過情境式與探究式的實作活動,學生不只「看見」科學,還能「做中學」與「用中學」:在設計、操作、資料蒐集與結果詮釋的完整流程中,培養批判思考、問題解決與跨域整合能力,這些皆是優質教育的核心素養。實驗本身採用可擴充的難度階梯與差異化任務,能兼顧不同基礎的學生,鼓勵積極參與、同儕協作與反思回饋,進而點燃對科學的好奇心,強化自我導向學習與終身學習動機。 進一步地,『洋流學』課程在教育與研究的連結上,直接支援 SDG 14「保育與永續利用海洋與海洋資源」。透過理解洋流的物理機制與生地化效應,學生能將觀測與分析成果轉譯為真實議題的認識與行動建議,例如: • 永續漁業管理:以洋流驅動的棲地變動、上升流(湧升流)與海洋鋒面(fronts)位置,推估漁場時空分布,支援漁撈努力的調適與資源評估。 • 海洋污染應對:利用流場與擴散模型理解漂浮污染物(如塑膠碎片、漏油)的傳輸路徑,提出更有效的預警與清除策略。 • 棲地與保護區規劃:以觀測與遙測資料辨識生態熱點、洄游走廊與高生產力區域,強化海洋保護區或管理分區的科學依據。 此一教育—研究—治理的鏈結,讓學生在學習過程中就能接觸「證據導向」的決策思維,理解科學如何化為公共利益,並在未來職涯中轉化為政策建議、社會溝通與在地實踐的能力。最終,學生既能以科學素養回應全球環境挑戰,也能以公民素養促進海洋資源的永續使用,共同推動 SDG4 與 SDG14 的落實。
永續影響力:「洋流學」課程以探究式與實作學習設計,讓學生在動手操作與數據分析中培養批判思考與跨域整合能力,契合SDG 4.1.1強調的「優質與包容教育」。課程鼓勵自主與終身學習,亦符合SDG 4.3.2中「向公眾開放教育活動、推廣終身學習」的精神。進一步結合海洋觀測與應用研究,學生將學習成果轉化為漁業管理、污染應對及棲地保護等實際行動,呼應SDG 14.2.2「保護並永續利用海洋資源」之核心目標,展現教育、研究與社會實踐的整合。
|
|
|
Evidence:


