14.5.3
1. 2025 Ocean Action Symposium
海洋素養與適能
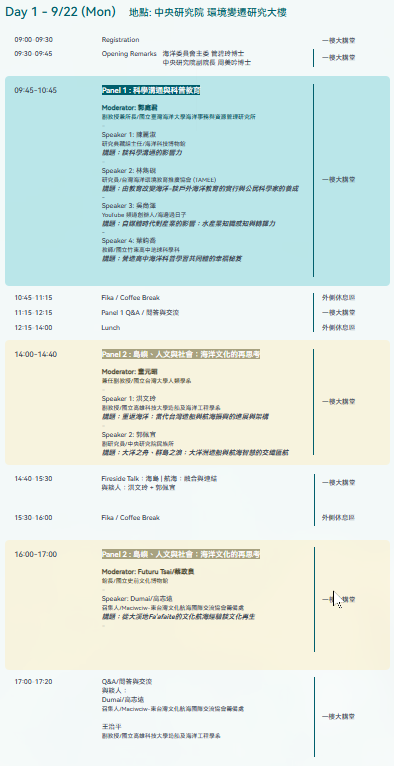
What is your vision of "ocean literacy"? Ocean literacy is more than just textbook knowledge; it's a way of looking at the world—it influences our values and shapes our motivation to act. Have you ever considered this? Every breeze, every current, every ship, every story of the sea—they are inextricably linked to our lives and culture. How do Taiwan's tides and ocean currents affect residents of the island and its outlying islands? How have shipbuilding and navigational technology shaped Taiwan's unique maritime culture? And what significance do coral conservation efforts have for the marine environment? This year's symposium invited scholars from across disciplines, educators on the front lines, representatives from the marine restoration industry, and marine cultural activists to share their insights! The symposium focused on themes of science communication and popular science education, marine culture and island society, and social participation and marine restoration.
Sustainable Impact:The "Ocean Literacy" symposium redefines ocean awareness as more than academic knowledge—it is a worldview that connects science, culture, and action. The event invited interdisciplinary experts, educators, and marine restoration practitioners to explore three key themes: science communication and public education, marine culture and island society, and social participation in ocean restoration.Through discussions on topics such as coral conservation, shipbuilding traditions, and community-based marine stewardship, the symposium encouraged participants to view the ocean as an integral part of life and identity.This initiative not only enhances public understanding of marine sustainability but also strengthens collaborations among academia, education, and industry.It exemplifies SDG 14 (Life Below Water) by promoting ocean conservation awareness, and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) by fostering multi-sector partnerships for sustainable ocean development and education.
你對「海洋素養」的想像是什麼? 海洋素養,不只是課本上的知識,更是一種看待世界的方式——它關係著我們的價值觀,也形塑了我們的行動力。 你有想過嗎?每一次吹來的海風、流動的洋流,每一艘航行的船隻、每一段海上故事,都與我們的生活與文化息息相關。台灣的潮汐與洋流,如何影響本島與離島的居民?造船與航海技術,如何塑造出台灣獨特的海洋文化?珊瑚保育的努力,對海洋環境又有什麼意義? 今年的座談邀請跨領域的學者、站在第一線的教育者、致力海洋復育產業代表與海洋文化行動者,帶來精彩的分享! 座談會主題聚焦在——科學溝通與科普教育、海洋文化與島嶼社會、社會參與與海洋復育
永續影響力:本次「海洋素養」主題座談強調從教育、文化、產業與社會參與等面向深化全民的海洋意識。活動以「你對海洋素養的想像是什麼?」為引言,鼓勵民眾重新思考海洋與人類生活的連結,將海洋視為理解世界與行動的出發點。座談邀集跨領域專家,包括海洋教育學者、文化研究者、海洋復育產業代表及第一線教育工作者,探討「科學溝通與科普教育」、「海洋文化與島嶼社會」及「社會參與與海洋復育」三大主題。內容涵蓋從海洋環境保育、珊瑚與生態修復、航海與造船文化,到地方社會行動等多層面議題。此座談會透過多元對話與知識交流,深化社會大眾對海洋永續的理解,並強化學術、教育與產業間的夥伴合作,實踐 SDG 14(保育與永續利用海洋資源) 與 SDG 17(強化全球夥伴關係) 的精神,推動從知識、文化到實踐的「海洋公民素養」。

Evidence:
https://www.oceanactionsymposium2025.com/
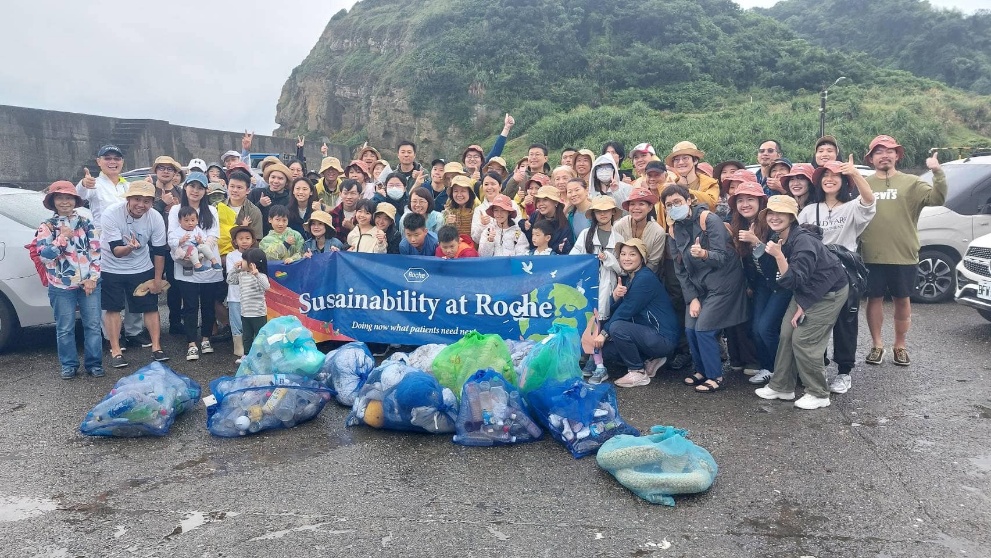
2. Phoenix Tours and Yulong No. 8 joined forces to lead ADLINK Technology (or: ADLINK) in a beach cleanup on Keelung Islet.
連結鳳凰旅遊與玉龍捌號帶領瑞傳科技登基隆嶼淨灘
Protecting the "Pearl of Taiwan": NTOU USR Team, Phoenix Tours, and "Yulong No. 8" Continue Five-Year Beach Cleanup Commitment Off the coast of northern Keelung lies Keelung Islet, a volcanic island of mysterious allure. Not only is it home to rare species like Silene morrisonmontana (Keelung Catchfly) and boasts rich geological features, but it is also widely regarded as the "Pearl of Taiwan." However, the accumulation of marine debris poses a persistent threat to this unique beauty. The National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU) USR Team fulfilled their five-year commitment by once again landing on the islet for a beach cleanup. They were joined by Phoenix Tours (Phoenix International Travel Agency) and the local boat owners of the recreational fishing vessel, Yulong No. 8. This event stands as a prime example of cross-sectoral collaboration, brilliantly integrating University Social Responsibility (USR), Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, and island tourism promotion. Despite the Keelung Islet hiking trail being temporarily closed due to damage from the April 3rd earthquake, ocean currents continue to deposit marine debris along the coastline. Professor Wang Hui-Chiao of the NTOU Department of Tourism led the students, personally demonstrating how to categorize the debris using the ICC (International Coastal Cleanup) classification system. The students served as guides, allowing participants to not only experience the islet's geological charm firsthand but also to understand the deep connection between industrial development and environmental sustainability before entering the workforce. This cleanup is a core objective of NTOU's "Three Prosperities of Fishery - International Blue Economy Demonstration Zone" USR project. The faculty and students are driven by a vision to ensure visitors "deeply remember" this stunning island, once one of the Eight Scenic Spots during the Japanese colonial era, through continuous environmental maintenance. With logistical support for waste removal provided by the Keelung District Fishermen's Association, 40 participants, including students, faculty, and industry professionals, worked together to clear debris accumulated along the coast. The effort yielded significant results, with a total of 85 plastic bottles, 7 kilograms of fishing nets, and over 12.5 kilograms of general garbage being collected. The NTOU USR Team firmly believes that only through sustained, collective maintenance can this "Pearl of Taiwan" welcome every visitor with its most pristine and beautiful appearance when the summit reopens, all while continuously supporting local fishermen and promoting the sustainable development of island tourism.
Sustainable Impact: The “Guarding Taiwan’s Dragon Pearl” cleanup project on Keelung Islet, jointly organized by NTOU’s USR team, Phoenix Tours, and local partners, exemplifies the objectives of SDG 14.3.2 and 14.5.3.
Through long-term collaboration between academia, industry, and community stakeholders, the initiative focuses on marine debris removal and environmental restoration, addressing marine pollution and promoting sustainable fisheries management. Students participated in the ICC waste classification process, combining hands-on environmental education with practical sustainability training.
This multi-stakeholder initiative integrates university social responsibility (USR), corporate ESG practices, and eco-tourism development, fostering awareness of the interdependence between industry and ecology. It demonstrates how continuous cooperation can protect marine biodiversity, empower local communities, and sustain Keelung Islet’s role as a model of blue economy and coastal resilience in Taiwan.
守護「臺灣龍珠」:海大USR、鳳凰旅遊與「玉龍捌號」的五年淨灘約定 在基隆北方外海,有一座充滿神秘色彩的火山島——基隆嶼,它不僅擁有「基隆蠅子草」等稀有植物和豐富的地質奇觀,更被譽為臺灣的「龍珠」。然而,海洋廢棄物卻威脅著這份獨特的美麗。 國立臺灣海洋大學USR團隊再次履行了他們的五年約定,偕同鳳凰國際旅行社及在地夥伴玉龍捌號休閒娛樂漁船的船家一同登島淨灘。這不僅是一場環境保護行動,更是一次將大學社會責任(USR)、企業社會責任(ESG)與島嶼觀光巧妙結合的異業合作典範。 儘管近期四月三日的地震導致基隆嶼登山步道受損暫停開放,但海漂垃圾並沒有停止隨洋流堆積。海大觀光系王彙喬老師帶領學生,親自示範如何進行海漂垃圾ICC分類。學生們在淨灘行動中扮演領航員的角色,不僅讓參與者親身感受基隆嶼的地景魅力,更在就業前深刻體認到產業發展與環境永續的密不可分。這次淨灘是海大「三漁興旺-國際藍色經濟示範區」USR計畫的核心一環。師生們懷抱著讓遊客「深深記住」這座曾為日治時期八景之一的美麗島嶼的願景,長期投入環境維護。在基隆區漁會的協助清運下,四十位師生與業者共同努力,成果豐碩:總計清除了八十五支保特瓶、七公斤漁網,以及超過十二公斤的各式垃圾。 海大USR團隊堅信,唯有持續的共同維護,才能讓這顆「臺灣龍珠」在重新開放登頂時,依然以最美好、最純淨的面貌,迎接每一位到訪的遊客,並持續帶動地方漁業與觀光永續發展。
永續影響力:本次「守護臺灣龍珠」基隆嶼淨灘行動,結合海大USR團隊、鳳凰旅遊與在地船家合作,符合 SDG14.3.2、14.5.3 之指標精神。活動以減塑與海漂垃圾清理為主軸,展現學校與社區、企業共同推動海洋污染防治與生態維護的實踐。師生親身參與ICC分類與淨灘行動,落實環境教育、永續漁業與生態旅遊結合之目標,建立公私協力的藍色經濟典範,促進地方產業與環境共榮。


Evidence: