13.3.4
- Investigation on coastal wetland carbon sink and establishment of measurement methodology 建立海岸濕地碳匯量測方法學研究
According to the Ministry of Agriculture''s key strategic action plan for Taiwan''s 2050 net-zero transition "Natural Carbon Sinks" released in April 2023, the current national greenhouse gas inventory report only includes forest carbon sink data in the "Land Use, Land-Use Change, and Forestry" section. Important carbon sink data for our country''s soil, ocean, and wetlands have not been included due to the lack of an MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, Verification) mechanism tailored to our environmental conditions, resulting in a lack of basic carbon sink inventory and annual variation data. Therefore, to understand the overall changes in carbon sequestration and the potential emission reductions in our country, it is essential to actively develop ocean carbon sink measurement methods, establish local coefficients, and develop baseline data. This project specifically targets coastal wetland carbon sinks (such as clam and oyster aquaculture) by conducting coastal wetland area surveys. Image recognition analysis showed overall accuracy (OA) between 80-90% and a Kappa coefficient ranging from 0.5-0.9. The bamboo raft area for oyster racks is approximately 285.3 hectares, and the hanging/suspended racks cover around 321.4 hectares. Analysis of coastal wetland carbon sink characteristics, carbon sink activity data, and local coefficients indicates that carbon storage capacities for oyster and clam farming are 353.98 ± 173.20 and 510.49 ± 474.42 t CO2e, respectively. The emission factor for CO2 are 1.52 ± 4.26 and 2.47 ± 8.32 t CO2e ha/yr, for CH4 are 1.31 ± 3.05 and 2.86 ± 6.97 t CO2e ha/yr, and for N2O are 0.16 ± 1.24 and -0.38 ± 0.92 t CO2e ha/yr, confirming that these systems are carbon sources. Through the execution of this project, we aim to construct baseline data for Taiwan's coastal wetlands, facilitating the future establishment of measurement and estimation methodologies, assessments of carbon sink enhancement potential, and verification protocols for carbon sink volumes.
Sustainable Impact: This project, aligned with Taiwan's 2050 Net-Zero Transition – Natural Carbon Sink Strategy, focuses on developing localized MRV systems (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) for coastal wetland carbon sinks, including clam and oyster aquaculture. Using satellite imagery and field data, the study established baseline datasets on carbon storage and greenhouse gas emissions, identifying both systems as net carbon sources.The results provide critical scientific evidence to improve national carbon accounting and enhance blue carbon management strategies. This initiative bridges scientific research with climate policy, filling data gaps in Taiwan's national greenhouse gas inventory.It directly supports SDG 13.3.1 (Enhancing climate education and awareness), 13.3.2 (Building climate research capacity), 13.3.3 (Developing MRV systems for climate monitoring), and 13.3.4 (Linking scientific data with policy implementation), demonstrating NTOU's leadership in advancing marine carbon science and supporting climate action through evidence-based research.
根據112年4月農業部發布之臺灣2050淨零轉型「自然碳匯」關鍵戰略行動計畫,目前我國國家溫室氣體清冊報告僅於《土地利用、土地利用變化及林業部門》章節中盤點及收納森林碳匯相關資料,我國土壤、海洋與濕地等重要碳匯量資料,因尚未依我國環境條件建立相符之MRV機制(Monitoring, Reporting, Verification),缺乏基礎碳匯量盤點及每年變動量等資料,因此,為瞭解我國整體碳匯變動量與可抵減之排放量,應積極建構海洋碳匯量測方法、建立本土係數與發展基線資料。本案針對海岸濕地碳匯(如文蛤與牡蠣養殖產業),進行海岸濕地面積調查,影像辨識結果顯示準確度OA多落在80-90%、Kappa係數落在0.5-0.9之間,竹筏式蚵架面積約為285.3公頃及平掛/垂吊式蚵架約為321.4公頃。分析其海岸濕地碳匯特性、碳匯活動數據及本土係數,結果顯示牡蠣及文蛤養殖之碳儲量分別為353.98±173.20 及510.49±474.42 t CO2e,二氧化碳排放係數分別為1.52±4.26及2.47±8.32 t CO2e ha /yr,甲烷分別為1.31±3.05及2.86±6.97 t CO2e ha /yr,氧化亞氮分別為0.16±1.24及-0.38±0.92 t CO2e ha /yr,皆為碳源(即碳排放)系統。透過本案之執行,期望可建構我國海岸濕地之基線資料,俾利未來建立量測與計量評估、增匯潛力估算與碳匯量認驗證方法之目標。
永續影響力:本計畫依據農業部「2050淨零轉型自然碳匯行動策略」,針對海岸濕地(包含文蛤與牡蠣養殖區)進行碳匯監測與盤查,透過影像辨識與統計模型,建立臺灣首批具本土化特徵的海洋碳匯基線資料。研究成果揭示不同養殖模式下的碳儲量與排放特性,並指出其仍屬碳源系統,顯示未來亟需增匯技術與碳管理優化。此研究有助於建構國家層級的海洋碳匯MRV機制(監測、通報、驗證),補足以往溫室氣體清冊中海洋與濕地碳匯資料的缺口,強化臺灣在氣候變遷下的碳管理與政策依據。本案呼應 SDG 13.3.1(提升氣候變遷教育與意識)、13.3.2(推動氣候行動研究能力)、13.3.3(建立氣候監測與驗證體系)、13.3.4(促進科學資料共享與政策連結),展現海洋大學在氣候科學與淨零實踐中的科研貢獻。


Evidence: https://www.frs.gov.tw/view.php?id=87&subtheme=&theme=FRS_FB&utm_source=chatgpt.com
- The Environmental Survey and Evaluation of the Nuclear Power Plant No. 4 Units 1 and 2 Power Generation Project – Supervision of the Short-Term Beach Nourishment at Yanliao Coa 核能四廠第一、二號機發電計畫環境調查評析–鹽寮海岸短期性養灘之監督工作
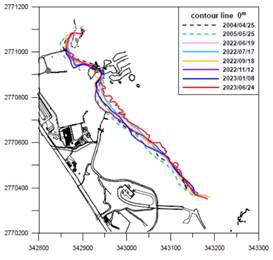
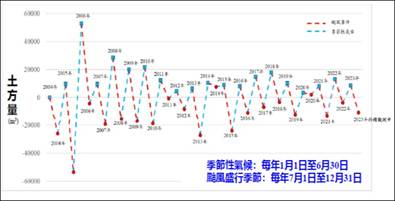
Based on the results of beach terrain monitoring over the years at Yenliao Beach in the Northeastern corner, it is evident that short-term variations in the monitored area are primarily attributed to typhoon events. The amount of sand and sediment variation varies depending on the path and scale of the typhoon events. Following these typhoon events, the beach terrain gradually shows signs of recovery and accretion as the influence of the northeastern monsoon weakens. The variations in sediment quantity and the position of the 0-meter contour line over the monitoring period are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2, respectively.
Sustainable Impact: This project monitored shoreline and geomorphological changes at Yanliao Beach (Northeast Coast, Taiwan) to assess the impact of typhoons and monsoons on coastal dynamics. The findings indicate that short-term changes are primarily caused by typhoon events, with variations in sediment loss depending on storm intensity and path. After typhoons, gradual sand recovery (accretion) occurs as the northeast monsoon weakens.The study recorded sediment volume changes and 0m shoreline shifts, building a long-term coastal monitoring database. These data provide critical references for coastal conservation, disaster prevention, and adaptation planning.By enhancing understanding of coastal vulnerability to extreme weather events, this work directly supports SDG 13.3.4, strengthening climate monitoring, risk assessment, and resilience-building for sustainable coastal management.
東北角鹽寮沙灘地形變動監測,根據歷年沙灘地形監測成果顯示:監測區鹽寮沙灘短期性變動因素為颱風事件,沙灘土砂變動量視颱風行徑及其規模有所差異,颱風事件後沙灘地形隨東北季風的減弱漸次呈現回淤變化,監測歷程之土砂量及0m灘線的變動情形分別如圖1及圖2所示。
永續影響力: 本計畫針對東北角鹽寮沙灘進行地形變動長期監測,以了解氣候變遷與颱風事件對海岸環境的影響。監測結果顯示,沙灘短期變化主要受颱風影響,不同颱風路徑與強度會導致沙灘侵蝕量的差異;而在颱風過後,隨東北季風減弱,沙灘呈現回淤現象。研究同時量測土砂變動量及0公尺灘線變化,建立長期監測資料庫,為未來海岸保育與防災規劃提供重要依據。此研究不僅提升對極端氣候事件下海岸地形反應的理解,也強化地方政府與研究單位在氣候監測、災害評估與永續海岸管理的能力,符合 SDG 13.3.4 所強調之氣候行動與適應性管理。
Evidence: https://oet.ntou.edu.tw/p/405-1061-104044,c7466.php?Lang=zh-tw
- Investigation on aquaculture carbon sink and establishment of measurement methodology 養殖漁業碳匯調查及建立量測方法學研究
Due to the absence of a matching Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) mechanism in our country, the national greenhouse gas emissions inventory has yet to establish wetland-related carbon sink data. In order to understand the overall carbon sink variations and potential reductions in emissions in our country, as well as to adhere to the three core principles (measurable, verifiable, and reportable) and five key characteristics (additivity, conservatism, permanence, avoidance of harm, and avoidance of double counting) required for future voluntary reduction projects, this project will focus on carbon sinks in aquaculture, including the milkfish and sea bass farming industries. We will measure the greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sinks in water bodies and sediments, and analyze their local coefficients. The goal is to accurately estimate the carbon sink or carbon source capabilities of wetlands in line with the international trend towards net-zero emissions and to achieve the domestic net-zero emissions policy objectives.
Sustainable Impact: This project addresses the current gap in Taiwan’s national greenhouse gas inventory, which lacks wetland carbon sequestration data. It focuses on measuring greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in milkfish and seabass aquaculture systems, including both water and sediment compartments, to establish localized carbon coefficients. The study supports the development of Taiwan’s Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) framework and aligns with the three key MRV principles—measurability, verifiability, and reportability—as well as the five essential attributes of carbon management: additionality, conservativeness, permanence, avoidance of leakage, and prevention of double counting.
The outcomes will enhance national understanding of wetland carbon fluxes, inform voluntary mitigation programs, and contribute to net-zero strategies under SDG 13.3–13.4. Simultaneously, the research advances sustainable aquaculture and coastal wetland carbon management, aligning with SDG 14.2–14.3. By quantifying blue carbon potential and integrating it into national climate policy, this project builds a scientific foundation for low-carbon aquaculture and climate-resilient marine ecosystems in Taiwan.
因我國尚未建立相符之監測、報告與驗證機制(MRV),國家溫室氣體排放清冊尚未建立濕地相關碳匯量數據,為了解我國整體之碳匯變動量及可減少之排放量,以及未來自願減量專案中所需之三大原則(可量測、可驗證、可報告)和五大特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免產生危害及避免重複計算),本案將針對養殖漁業碳匯,包含虱目魚及鱸魚養殖產業,進行水體及底土之溫室氣體與碳匯量測,並分析其本土係數,期望可精確的推估濕地的碳匯或碳源能力,以符合國際淨零排放趨勢及達到國內淨零排放政策目標。
永續影響力: 本計畫針對我國尚未納入國家溫室氣體清冊之「濕地碳匯」議題,進行養殖漁業(虱目魚與鱸魚產業)水體與底土之溫室氣體排放與碳匯量測,建立本土化碳吸存係數,補足我國MRV(監測、報告、驗證)機制缺口。研究結果將有助於掌握濕地碳源與碳匯變動,為自願減量專案奠定基礎,符合「可量測、可驗證、可報告」三原則及五項碳管理特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免危害、避免重複計算)。 此研究不僅支援國家淨零排放政策與氣候治理(SDG13.3.1–13.4.1),亦促進海岸與養殖濕地的生態碳匯功能理解(SDG14.2.1–14.3.3),為台灣藍碳管理與低碳漁業發展提供重要實證依據。


Evidence:
http://bit.ly/3LhXwgG