14.2.1
1. Maritime Renewable Energy Alliance Center-Energy Turnover PBL Workshop
113年度海域再生能源聯盟中心-能源翻轉PBL工作坊 海域再生能源開發與海岸帶居民生活衝擊與調適
In the night state, images are not clearly recognized by computer vision. Therefore, this technology uses a UAV based a lidar to detect nighttime environmental information and recognize human characteristics. Using the background difference method and the algorithm of density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), the root mean square error and the surface state of the object are summarized as a condition to judge whether the object is human. The artificial intelligence algorithm of faster region-based convolutional neural network (Faster R-CNN) is used for skeleton recognition, and an automatic recognition system is established. As a result, the human-body recognition results of surface analysis and skeleton recognition are both up to 87.5 % in the nighttime environment. The website information of recognition results is established through the server terminal computer to present the current measured environmental state and recognize whether there is a human body in the nighttime environment. Eventually, the technology is applied to search the victims in the disaster relief environment and reduce the difficulty and time of night search and rescue.
Sustainable Impact: This technology employs LiDAR-equipped drones for nighttime detection, capable of identifying human features under low-light conditions to enhance disaster rescue efficiency and environmental monitoring. It aligns with SDG 13.3.1 by advancing education and technological application for climate adaptation and emergency response. The system's use of 3D surface fitting and spatial clustering supports SDG 14.2.1, contributing to coastal and terrestrial ecosystem monitoring. Through AI-based object recognition and data-sharing web platforms, it fulfills SDG 17.2.5's focus on interdisciplinary research collaboration and technological partnerships. Moreover, its energy-efficient, light-independent sensing capability exemplifies SDG 7.4.1, promoting innovative clean technology solutions for sustainable environmental management.
由於在夜間狀態下,電腦視覺無法明確判別物體的存在,然而光達可透過雷射掃瞄而不受光線影響。因此,本技術利用無人機以光達作為感測器主軸,以探測夜間環境資訊及辨別人體特徵。利用背景差分法和基於密度的空間聚類演算法(DBSCAN),透過曲面擬合計算出均方根誤差,歸納出物體表面狀態,作為判斷物體是否為人的一個條件。然後將其點雲資料進行影像處理,並以目標檢測法(Faster R-CNN)對形貌進行訓練及辨識,根據人體和物體特徵建立自動化辨識系統。最終,在夜間環境狀態下可即時測量出人體,並獲得最佳表面分析與骨架辨識成功率均有87.5%。並且透過伺服端電腦建立網站連結,呈現當下量測的環境狀態及識別環境是否存在人體,其效益可應用在救災環境下搜索罹難者,減少夜間搜救的困難及時間。
永續影響力:此技術以光達搭載無人機進行夜間偵測,能在低光環境下辨識人體特徵,提升救災效率與環境監測能力,符合SDG 13.3.1推動氣候災害應變教育與技術應用的目標;同時,其環境掃描與地表曲面擬合分析有助於沿岸與陸地生態監測,呼應SDG 14.2.1對海洋與濱海系統的保護研究;此外,系統整合AI影像辨識與資料共享平台,展現SDG 17.2.5強調的跨領域技術合作;而其高效率、低照度運作特性亦符合SDG 7.4.1提倡的智慧能源與永續科技創新應用。




Evidence: https://www.facebook.com/energyntou/
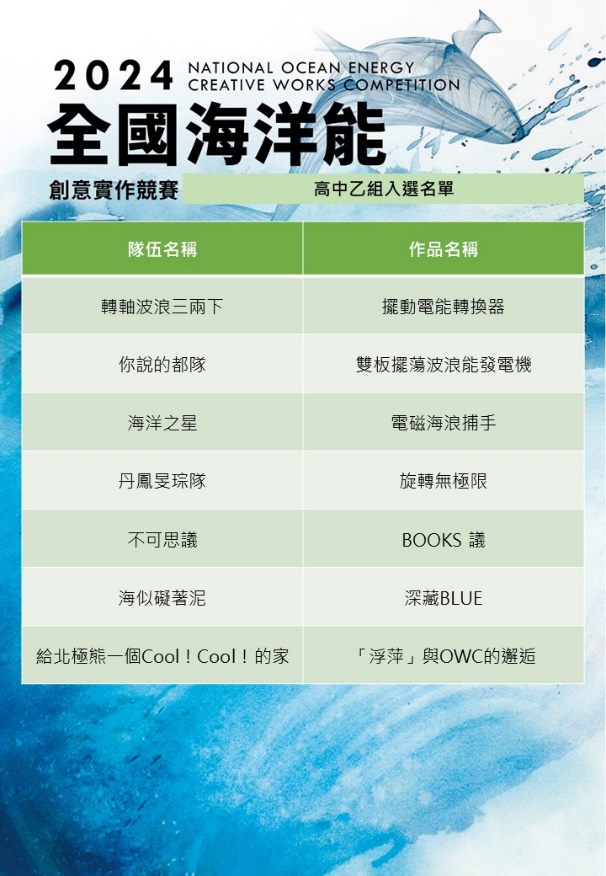
2. National Ocean Energy Creative Implementation Competition
全國海洋能創意實作競賽
The Competition: Starting in the year 2016 (Republic of China 105), National Taiwan Ocean University, in collaboration with the Keelung City Government, jointly organized this competition and expanded it to include participants from national
Sustainable Impact:Since 2011, National Taiwan Ocean University has organized the Marine Energy Competition, focusing on wave and current energy converter design, efficiency optimization, and cost analysis. This long-standing event fosters innovation and hands-on learning among students, encouraging the application of marine energy technologies to support clean energy transitions. The competition strengthens awareness of renewable ocean energy's role in mitigating climate change while building practical engineering and sustainability skills. Moreover, it enhances collaboration between academia and industry in developing marine energy innovations. This initiative supports SDG 7.4.1 (clean energy promotion), SDG 13.3.1 (climate action education), SDG 14.2.1 (sustainable use of marine resources), and SDG 17.2.5 (partnerships for sustainable technology development).
海洋能源競賽的開始:自民國100年起,海洋大學開始舉辦海洋能源相關競賽。這競賽涵蓋了波能和流能轉換器的設計、效率計算、成本和安裝等領域。這個競賽已經持續多年,並取得了豐碩的成果。
永續影響力:自民國100年起,國立臺灣海洋大學持續舉辦「海洋能源競賽」,主題涵蓋波能與流能轉換器設計、效率分析、成本評估與安裝技術等領域。活動旨在培育學生的創新思維與實作能力,促進海洋再生能源技術的發展。透過競賽形式,學生得以實踐工程理論,並理解海洋能源於減緩氣候變遷及永續能源轉型中的關鍵角色。活動亦促進學術與產業界在永續技術研發上的交流合作。此舉落實 SDG 7.4.1「推廣潔淨能源技術」、SDG 13.3.1「提升氣候行動教育」、SDG 14.2.1「保育與永續利用海洋資源」及 SDG 17.2.5「強化夥伴關係推動永續科技創新」。

Evidence:
https://www.facebook.com/energyntou/
3. 2025 Ocean Action Symposium
海洋素養與適能
What is your vision of "ocean literacy"? Ocean literacy is more than just textbook knowledge; it's a way of looking at the world—it influences our values and shapes our motivation to act. Have you ever considered this? Every breeze, every current, every ship, every story of the sea—they are inextricably linked to our lives and culture. How do Taiwan's tides and ocean currents affect residents of the island and its outlying islands? How have shipbuilding and navigational technology shaped Taiwan's unique maritime culture? And what significance do coral conservation efforts have for the marine environment? This year's symposium invited scholars from across disciplines, educators on the front lines, representatives from the marine restoration industry, and marine cultural activists to share their insights! The symposium focused on themes of science communication and popular science education, marine culture and island society, and social participation and marine restoration.
Sustainable Impact:The "Ocean Literacy" symposium redefines ocean awareness as more than academic knowledge—it is a worldview that connects science, culture, and action. The event invited interdisciplinary experts, educators, and marine restoration practitioners to explore three key themes: science communication and public education, marine culture and island society, and social participation in ocean restoration.Through discussions on topics such as coral conservation, shipbuilding traditions, and community-based marine stewardship, the symposium encouraged participants to view the ocean as an integral part of life and identity.This initiative not only enhances public understanding of marine sustainability but also strengthens collaborations among academia, education, and industry.It exemplifies SDG 14 (Life Below Water) by promoting ocean conservation awareness, and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) by fostering multi-sector partnerships for sustainable ocean development and education.
你對「海洋素養」的想像是什麼? 海洋素養,不只是課本上的知識,更是一種看待世界的方式——它關係著我們的價值觀,也形塑了我們的行動力。 你有想過嗎?每一次吹來的海風、流動的洋流,每一艘航行的船隻、每一段海上故事,都與我們的生活與文化息息相關。台灣的潮汐與洋流,如何影響本島與離島的居民?造船與航海技術,如何塑造出台灣獨特的海洋文化?珊瑚保育的努力,對海洋環境又有什麼意義? 今年的座談邀請跨領域的學者、站在第一線的教育者、致力海洋復育產業代表與海洋文化行動者,帶來精彩的分享! 座談會主題聚焦在——科學溝通與科普教育、海洋文化與島嶼社會、社會參與與海洋復育
永續影響力:本次「海洋素養」主題座談強調從教育、文化、產業與社會參與等面向深化全民的海洋意識。活動以「你對海洋素養的想像是什麼?」為引言,鼓勵民眾重新思考海洋與人類生活的連結,將海洋視為理解世界與行動的出發點。座談邀集跨領域專家,包括海洋教育學者、文化研究者、海洋復育產業代表及第一線教育工作者,探討「科學溝通與科普教育」、「海洋文化與島嶼社會」及「社會參與與海洋復育」三大主題。內容涵蓋從海洋環境保育、珊瑚與生態修復、航海與造船文化,到地方社會行動等多層面議題。此座談會透過多元對話與知識交流,深化社會大眾對海洋永續的理解,並強化學術、教育與產業間的夥伴合作,實踐 SDG 14(保育與永續利用海洋資源) 與 SDG 17(強化全球夥伴關係) 的精神,推動從知識、文化到實踐的「海洋公民素養」。

Evidence:
https://www.oceanactionsymposium2025.com/
4. Mao-ao Caspian Sea ESG Travel Family Itinerary
卯澳里海ESG旅遊親子行程
This activity includes an observation of intertidal organisms in the Ma-gang intertidal zone, a cultural and ecological tour of the Mao-ao community, beach and stream cleaning, and a traditional haenyeo underwater collection and snorkeling experience. Fifty people from Cathay Life Insurance participated, with instructors Dr. Xiao Yaoren and Dr. Shikina Shinya providing explanations.
Sustainable Impact:The event featured intertidal biodiversity observation, community cultural and ecological tours, beach and stream cleanups, and traditional underwater harvesting and snorkeling experiences. Guided by professors Hsiao Yao-Jen and Shikina Nobuya, participants gained hands-on understanding of marine ecosystems and coastal culture. This activity effectively integrates local knowledge, ecological education, and conservation action, encouraging public participation in marine stewardship. By raising awareness of ecosystem protection through experiential learning, it aligns with SDG 14.2.1, which emphasizes the sustainable management and restoration of coastal and marine ecosystems. The initiative exemplifies how higher education institutions can bridge science, community engagement, and environmental responsibility.
本次活動項目:馬崗潮間帶生物觀察、卯澳社區文化與生態導覽/淨灘淨溪、傳統海男海女水下採集暨浮潛體驗。「國泰人壽」計50人參與,本計畫蕭堯仁老師、識名信也老師現場解說。
永續影響力:活動內容涵蓋潮間帶生物觀察、社區文化與生態導覽、淨灘淨溪以及傳統潛水採集體驗,兼具環境教育與實地保育行動。透過教師現場講解,參與者深入了解海岸生態與人文互動,強化保育意識與公民責任。此活動將地方知識、科學教育與生態實踐相結合,促進社會大眾對海洋環境的理解與守護,符合 SDG 14.2.1「加強海洋與沿岸生態系的永續管理與復育」,展現大學推動公民科學與環境教育的實踐力。


Evidence:
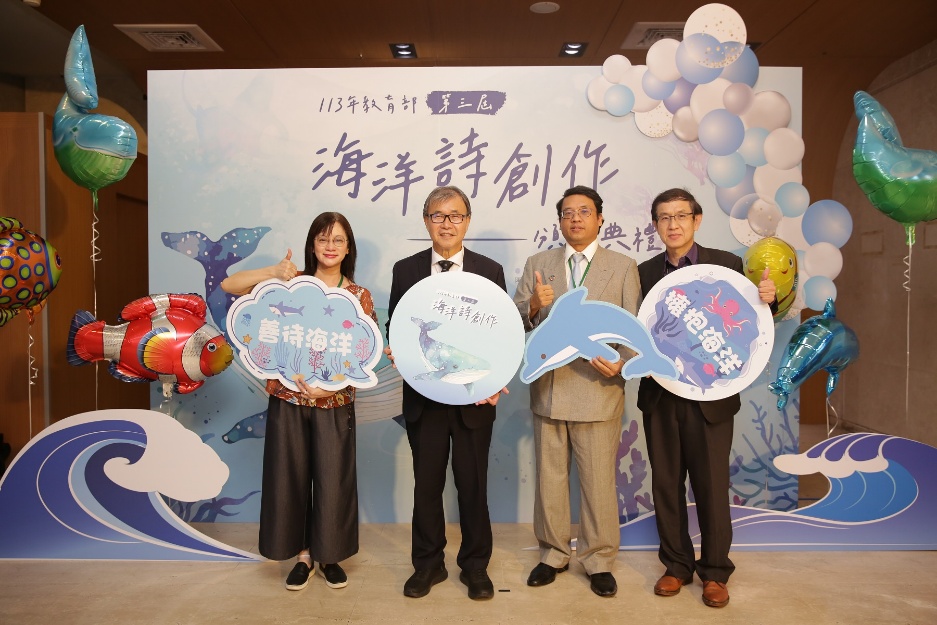
5. The Third Ocean Poetry Award Ceremony
第三屆海洋詩頒獎典禮
The 3rd Ocean Poetry Awards Ceremony To echo and promote the ideals of caring for the ocean and fostering ocean sustainability, the Ministry of Education held the 3rd Ocean Poetry Awards Ceremony on June 5, 2024, at the B1 Multi-Function Auditorium of the National Central Library. The event recognized and celebrated the outstanding achievements of the award-winning teachers and students. The theme of this year's Ocean Poetry Contest was “Sustainable Ocean.” Through a three-stage review process—including preliminary, secondary, and final evaluations—a total of 66 winning works were selected: 18 from the elementary school group, 18 from the junior high school group, 15 from the senior high school group, 8 from the college group, and 7 from the teacher group.
Sustainable Impact: The 3rd Marine Poetry Competition, organized by the Ministry of Education and themed “Sustainable Ocean,” exemplifies SDG 14.2.1, which emphasizes engaging communities and educational institutions in promoting sustainable marine practices.
By inviting students and teachers nationwide to express their reflections on ocean conservation through poetry, the event fosters environmental awareness and emotional connection to marine sustainability. The multi-stage selection process and recognition ceremony encourage creativity, participation, and interdisciplinary dialogue across all educational levels.
Through artistic expression and cultural engagement, the competition strengthens public understanding of the importance of protecting marine ecosystems, demonstrating how education and the arts can jointly advance the values of sustainability and ocean stewardship.
為響應推廣愛護海洋、永續海洋的理念,教育部於113年6月5日於國家圖書館B1多功能展演廳舉辦「第三屆海洋詩創作」頒獎典禮,嘉勉獲獎師生。本屆海洋詩創作徵選以「永續海洋」為主軸,歷經初審、複審及決審三道評選程序,評選出國小組18件、國中組18件、高中組15件、大專組8件及教師組7件,共66件獲獎作品。
永續影響力:教育部舉辦「第三屆海洋詩創作」徵選與頒獎典禮,以「永續海洋」為主題,鼓勵全國師生以詩歌創作表達對海洋環境的關懷與守護,符合 SDG14.2.1 所倡導之「推動社區與教育機構參與海洋永續行動」。此活動結合藝術與環保教育,透過文學形式深化公眾對海洋保育與永續發展的認識,促進不同教育階段師生的參與與交流,展現文化創作在推動海洋永續意識中的重要作用。


Evidence:
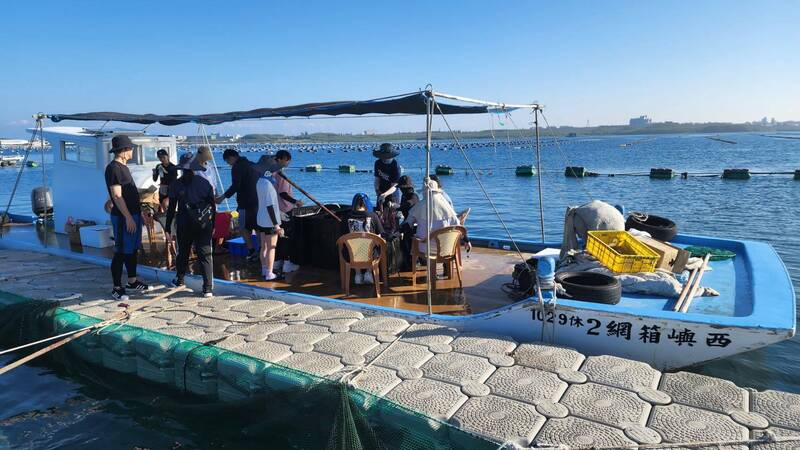
6. Fish fry tagging and releasing
魚苗標識與放流
Fry release has always been one of the most effective ways to restore fishery resources. By increasing the amount of fry added to the hatchery, the amount of economic fish species can be increased, and through the intermediate cultivation of box-net culture, the fry can grow to a larger size. Finally, its survival rate can be greatly improved. In the past, there were not many studies on the effects of fry release on fishery resource proliferation. In order to effectively evaluate the feasibility of offshore wind farms to develop marine pastures, the Changhua District Fisheries Association worked with the National Taiwan Ocean University and Taiwan Electric Power Company to select an offshore wind farm located off the coast of Changhua Fangyuan. Taipower's Phase I Demonstration Wind Farm in the Yun-Chang Uplift sea area uses identification and release of fish fry, combined with genetic testing technology, to evaluate the habitat utilization and fishery resource proliferation effects of fish fry on the offshore wind farm.
Sustainable Impact: The collaborative project between the Changhua Fishermen’s Association, National Taiwan Ocean University, and Taiwan Power Company exemplifies SDG 14.2.1, which promotes the participation of communities and educational institutions in sustainable marine actions.
Through fish fry release and recovery at the Taipower offshore wind farm in the Yun-Chang Uplift area, the initiative integrates tagging and genetic analysis to evaluate habitat utilization and fishery stock enhancement. This partnership bridges academia, government, and industry, advancing sustainable resource management and biodiversity restoration in offshore environments.
By combining renewable energy development with marine conservation, the project demonstrates how scientific innovation and cooperative action can simultaneously support ecological resilience, fishery revitalization, and sustainable blue economy development.
魚苗放流一直是漁業資源復育最有效方式之一,藉由增加孵育場的魚苗加入量,可提高經濟魚種的資源量,而透過箱網養殖的中間育成,讓魚苗成長至較大體型後,更可大幅提高其存活率。過去魚苗放流對漁業資源增殖的相關研究不多,為有效評估離岸風場發展海洋牧場的可行性,彰化區漁會與國立臺灣海洋大學及台灣電力公司共同合作,選定位於彰化芳苑外海雲彰隆起海域的台電一期示範風場,藉由魚苗標識放流回收結合基因檢測技術,評估魚苗對離岸風場的棲地利用與漁業資源增殖成效。
永續影響力:本計畫由彰化區漁會、國立臺灣海洋大學及台灣電力公司共同合作,於離岸風場實施魚苗放流與回收研究,符合 SDG14.2.1「推動社區或教育機構參與海洋永續行動」之精神。此行動結合產官學三方力量,以標識放流與基因檢測技術評估魚苗棲地利用與漁業增殖效益,展現對海洋資源永續利用的實質貢獻。計畫促進科學研究與漁業管理結合,推動綠能與海洋生態平衡共存。


Evidence:
https://news.ltn.com.tw/news/life/breakingnews/4359476
https://www.penghutimes.com/Article/Detail/30412
7. Workshop for New Southbound Policy
新南向工作坊
Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia are all surrounded by the ocean, and their coastal zones and fishing communities are highly vulnerable to climate change (particularly global warming). This makes them excellent observation and comparison areas for Taiwan's coastal environmental impacts and adaptation to climate change. By inviting scholars from the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia to participate in aquaculture, fisheries, and biodiversity research, Taiwan will be able to compare and absorb the similarities and differences in international socio-ecological system data collection and analysis, industrial development experience, and analyze the coupled effects of climate change on ecology, socio-economics, and vulnerability.
Sustainable Impact:This collaborative initiative among Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia aligns with SDG 14.2.1, which emphasizes educational and community-based actions supporting the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems.
By engaging scholars to compare coastal and fisheries systems across tropical island nations, the project enhances understanding of how climate change impacts marine ecology, fisheries, and socio-economic resilience. The initiative facilitates regional knowledge exchange on biodiversity conservation, aquaculture adaptation, and community vulnerability assessment.
Through comparative research and data sharing, it strengthens interdisciplinary collaboration in marine science and supports evidence-based strategies for coastal adaptation and sustainability, demonstrating higher education’s pivotal role in advancing marine ecosystem protection through education and research.
我國與菲律賓、馬來西亞、印尼均四周環海,海岸帶及漁村極易受到氣候變遷(特別是暖化效應)的影響,是可供我國因應氣候變遷在海岸帶環境衝擊與調適的極佳觀測或比對區域。透過安排的菲律賓、馬來西亞、印尼等學者之於養殖、漁業與生物多樣性議題則能提供我國比對與吸收國外社會生態系統資料收集分析與產業發展經驗之異同及氣候變遷效應在生態、社會經濟與脆弱度等面向之耦合分析能力。
永續影響力:本計畫以我國及菲律賓、馬來西亞、印尼等海島國家為比較對象,透過學者交流與資料比對,分析氣候變遷對海岸帶生態及漁村社會的影響,符合 SDG14.2.1 所強調的「推動社區與教育機構參與水域永續教育與實踐」。此跨國研究深化對氣候暖化下海洋生態脆弱性的理解,並促進區域間在漁業管理、生物多樣性及社會韌性方面的知識共享,展現大學在推動海洋環境教育與永續研究的積極角色。


Evidence:
https://oia.ntou.edu.tw/p/412-1022-6961.php?Lang=zh-tw
8. Yilan Green Expo Marine Waste Jigsaw Puzzle Lesson Plan
綠色博覽會海廢拼圖教案實作
The team collaborated with volunteers from Wave of the Sea and the Ocean Heart Association for Environmental Sustainability to conduct the “Marine Debris Puzzle” environmental education program at the Yilan Green Expo. Through interactive teaching and hands-on activities, participants learned about marine life and marine debris via a puzzle game, gaining awareness of the impact of waste on marine ecosystems. The program also encouraged sustainable actions such as reducing plastic use in daily life. This initiative not only enhanced public awareness of ocean conservation and environmental sustainability but also demonstrated effective cross-sector collaboration in advancing environmental education.
Sustainable Impact: National Taiwan Ocean University collaborated with “Hai Bo Lang” and the “Ocean Heart Environmental Sustainability Association” volunteers to conduct the “Marine Waste Puzzle” environmental education program at the Yilan Green Expo. Through interactive teaching and hands-on puzzle activities, participants learned about marine biodiversity, the impact of marine debris, and practical ways to reduce plastic waste in daily life.
The program promotes environmental awareness and community participation, aligning with SDG 14.2.1 – Marine Conservation and Ecological Education.
By integrating experiential learning and public engagement, the initiative enhances climate literacy and ocean stewardship, demonstrating the university’s role in fostering sustainability education and inspiring collective action toward a cleaner and more resilient marine environment.
團隊攜手「海波浪」及「海洋之心環境永續發展協會」志工夥伴,共同於宜蘭綠色博覽會執行「海廢拼圖」環境教育課程。活動以互動教學與實作體驗的方式,透過拼圖遊戲讓參與者認識海洋生物與海洋廢棄物,進而瞭解廢棄物對海洋生態造成的影響,並學習如何在日常生活中減少廢棄物產生、落實減塑行動。此課程不僅提升大眾對海洋保育與環境永續的意識,也展現跨部門協作推動環境教育的實踐成果。
永續影響力:國立臺灣海洋大學攜手「海波浪」與「海洋之心環境永續發展協會」志工於宜蘭綠色博覽會共同執行「海廢拼圖」環境教育課程,透過互動教學與拼圖遊戲,讓民眾認識海洋生物與海洋廢棄物對生態的影響,並學習減塑與環境保護行動。此活動結合教育推廣與公民參與,符合SDG14.2.1 海洋生態與保育教育 指標精神,強化社會大眾對氣候變遷與海洋保育的理解,推動環境永續行動力。

Evidence:
https://yilangreenexpo.e-land.gov.tw/class/28.html
9. Taiwan Smart Agriweek
臺灣國際漁業產業展
National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU), under the theme “Sustainable Ocean and Blue Health,” echoed the conference's five core values — S.M.A.R.T. (Sustainability, Market, Advancement, Resilience, and Technology) — at booth K816, showcasing its latest research and technological innovations in marine technology, fisheries ecology, and ocean health.
This year, NTOU presents 15 sustainable technology achievements and collaborates with six university–industry innovation platforms, demonstrating Taiwan's commitment to marine ecological protection and sustainable development goals (SDGs).
In addition, NTOU organized the 5th Marine Aquaculture Forum on September 12, bringing together experts from various disciplines to discuss how marine resource management and aquaculture innovation can contribute to carbon reduction and ocean sustainability.
Sustainable Impact: National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU) participated in the exhibition under the theme “Sustainable Ocean and Marine Health”, echoing the conference’s S.M.A.R.T. goals—Sustainability, Market, Advancement, Resilience, and Technology. At booth K816, NTOU showcased 15 cutting-edge research outcomes in marine technology, fisheries ecology, and ocean health, alongside six industrial partners from its research commercialization platforms.
On September 12, the university also hosted the 5th Marine Aquaculture Forum, bringing together experts to discuss strategies for carbon reduction through marine resource management and sustainable aquaculture.
This initiative aligns with SDG 14.2.1 – Marine Conservation and Ecological Education, highlighting NTOU’s leadership in advancing scientific innovation, promoting ocean conservation, and fostering academia–industry collaboration toward sustainable ocean development and blue carbon goals.
國立臺灣海洋大學以「永續海洋大健康」為主題,呼應大會「S.M.A.R.T.(永續、市場、前瞻、韌性與科技)」五大訴求,於攤位編號K816展示在海洋科技、漁業生態及海洋健康領域的最新研究與技術成果。此次,海大共展出15項技術成果,並有6家科研產業化平台的廠商共同參展,讓國內外業者見證海洋大學在保護海洋生態、推動永續發展方面的卓越貢獻。此外,海大在9月12日舉辦的「第五屆海水養殖論壇」,匯聚各領域專家,探討如何通過海洋資源管理和水產養殖來實現碳減排的目標。
永續影響力:國立臺灣海洋大學以「永續海洋大健康」為主題參與展會,展示15項海洋科技與漁業生態相關技術成果,並與6家科研產業化平台廠商共同參展,展現海大在海洋保育與永續發展領域的研究實力。活動期間舉辦「第五屆海水養殖論壇」,邀集專家探討透過資源管理與養殖技術達成碳減排目標。此舉符合 SDG14.2.1 保育與海洋生態教育行動,展現學校以科研推動生態保育、產學合作與永續海洋治理之具體實踐。


Evidence:
https://mprp.ntou.edu.tw/p/404-1017-103957.php?Lang=zh-tw
10. Investigation on aquaculture carbon sink and establishment of measurement methodology
養殖漁業碳匯調查及建立量測方法學研究
Due to the absence of a matching Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) mechanism in our country, the national greenhouse gas emissions inventory has yet to establish wetland-related carbon sink data. In order to understand the overall carbon sink variations and potential reductions in emissions in our country, as well as to adhere to the three core principles (measurable, verifiable, and reportable) and five key characteristics (additivity, conservatism, permanence, avoidance of harm, and avoidance of double counting) required for future voluntary reduction projects, this project will focus on carbon sinks in aquaculture, including the milkfish and sea bass farming industries. We will measure the greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sinks in water bodies and sediments, and analyze their local coefficients. The goal is to accurately estimate the carbon sink or carbon source capabilities of wetlands in line with the international trend towards net-zero emissions and to achieve the domestic net-zero emissions policy objectives.
Sustainable Impact: This project addresses the current gap in Taiwan’s national greenhouse gas inventory, which lacks wetland carbon sequestration data. It focuses on measuring greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in milkfish and seabass aquaculture systems, including both water and sediment compartments, to establish localized carbon coefficients. The study supports the development of Taiwan’s Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) framework and aligns with the three key MRV principles—measurability, verifiability, and reportability—as well as the five essential attributes of carbon management: additionality, conservativeness, permanence, avoidance of leakage, and prevention of double counting.
The outcomes will enhance national understanding of wetland carbon fluxes, inform voluntary mitigation programs, and contribute to net-zero strategies under SDG 13.3–13.4. Simultaneously, the research advances sustainable aquaculture and coastal wetland carbon management, aligning with SDG 14.2–14.3. By quantifying blue carbon potential and integrating it into national climate policy, this project builds a scientific foundation for low-carbon aquaculture and climate-resilient marine ecosystems in Taiwan.
因我國尚未建立相符之監測、報告與驗證機制(MRV),國家溫室氣體排放清冊尚未建立濕地相關碳匯量數據,為了解我國整體之碳匯變動量及可減少之排放量,以及未來自願減量專案中所需之三大原則(可量測、可驗證、可報告)和五大特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免產生危害及避免重複計算),本案將針對養殖漁業碳匯,包含虱目魚及鱸魚養殖產業,進行水體及底土之溫室氣體與碳匯量測,並分析其本土係數,期望可精確的推估濕地的碳匯或碳源能力,以符合國際淨零排放趨勢及達到國內淨零排放政策目標。
永續影響力:本計畫針對我國尚未納入國家溫室氣體清冊之「濕地碳匯」議題,進行養殖漁業(虱目魚與鱸魚產業)水體與底土之溫室氣體排放與碳匯量測,建立本土化碳吸存係數,補足我國MRV(監測、報告、驗證)機制缺口。研究結果將有助於掌握濕地碳源與碳匯變動,為自願減量專案奠定基礎,符合「可量測、可驗證、可報告」三原則及五項碳管理特性(外加性、保守性、永久性、避免危害、避免重複計算)。 此研究不僅支援國家淨零排放政策與氣候治理(SDG13.3.1–13.4.1),亦促進海岸與養殖濕地的生態碳匯功能理解(SDG14.2.1–14.3.3),為台灣藍碳管理與低碳漁業發展提供重要實證依據。


Evidence:
https://mprp.ntou.edu.tw/p/404-1017-108824.php?Lang=zh-tw&utm_source
11. Fish Culture Education Activities - Assisting with STEAM Curriculum for the Entire Semester
環教課程設計及環境教育設施場所申請會議
Through an inventory of the natural ecology and cultural history of Yilan''s coastal communities, an environmental education curriculum was designed to integrate local tourism resources to promote environmental education, and assistance was provided to fishing village communities in designing a self-operated survey of the biological composition of trolling fish caught along Taiwan''s coast. As this project continues to collaborate with community environmental education facilities, the community has voluntarily expanded the establishment of a sustainable management model for trolling on Yilan''s coastal beaches and worked closely with other local communities to actively promote environmental education courses, create local sustainable tourism highlights, cultivate local sustainable talents, and implement the concept of sustainable fishery culture, making the community a sustainable management site for fishing villages.
Sustainable Impact: This project integrates the natural ecology and cultural heritage of coastal Yilan communities to design environmental education programs that align with local tourism and sustainability goals. By developing a community-led coastal seine fish catch survey, it empowers fishing villages to conduct long-term monitoring of marine biodiversity. Through partnerships with local environmental education facilities, the initiative promotes community-driven sustainable management of coastal ecosystems and facilitates collaboration among neighboring villages.
Beyond environmental education, the program supports eco-tourism development, intergenerational learning, and local capacity building, cultivating community members as stewards of sustainable fisheries and marine heritage. The initiative embodies SDG 14.2.1, which emphasizes education and outreach supporting aquatic ecosystem conservation, freshwater and coastal resource management, and long-term sustainability through participatory community engagement.
透過宜蘭沿海社區的自然生態及人文歷史進行盤點,設計環境教育課程以整合在地觀光資源推廣環境教育,並協助漁村社區設計可自行運作之台灣沿海牽罟漁獲生物組成調查,隨著本計畫與社區環教設施場域合作持續推動,該社區自願擴大宜蘭沿岸沙灘牽罟的永續經營模式之建立與其他在地社區密切合作,積極推廣環境教育課程,打造地方永續觀光亮點,培育在地永續人才,落實漁業文化永續之概念,使社區成為漁村永續經營場域。
永續影響力:本計畫以宜蘭沿海社區為基地,結合當地自然生態與人文歷史進行資源盤點,設計具在地特色的環境教育課程,並協助漁村社區建立可自營運的「沿海牽罟漁獲生物組成調查」機制。計畫推動過程中促進社區環境教育設施合作與在地參與,社區進而自願擴大沿岸永續經營模式,並與周邊社區共享經驗。透過此行動不僅推廣永續觀光與海洋教育,也培育地方永續人才,促進漁業文化保存與生態意識提升。此計畫充分展現 SDG14.2.1 所倡導之「以教育與社區服務推動水域生態系統之永續管理/保護」。

Evidence:
https://www.oca.gov.tw/ch/home.jsp?id=371&parentpath=0,296,370&mcustomize=ocamaritime_view.jsp&dataserno=202401310001